随時更新
2017 PindelとPlatypusのフローを修正。
2018 brew tap 修正 ,reebayes、lumpyの誤りを修正。誤字修正。 lumpyの流れを見やすく修正。
2019インストール追記, lumpy -svのdockerイメージリンク追加, breseq dockerイメージの使用例追加, 誤字修正とリンク追加
2020 5/14 breseqのコマンド修正
2021 Platypusのインストール方法を修正
構造変異検出ツールのパフォーマンスを比較したペーパーが出ている。
実際に導入して、パフォーマンスを比較してみる。
以下のツールを紹介する。
- Breakdancer
- Pindel
- GASVpro
- LUMPY
- Hydra-sv
- DELLY2
- Platypus
- fermikit
- FreeBayes
- SvABA
- VarScan
- Breseq
- Scalpel
- Breakseek
- Scanindel
- PRISM
追記
- RAPTER-SV 構造変化の検出ツール
- Seeksv ソフトクリップ情報からSVを検出
- Discover de novoアセンブルしてバリアントをコール
- SVelter 様々なSVサブタイプを検出
- Sprites ソフトクリップから複雑な欠失を検出
- TIDDIT 様々な構造変化を検出
- Vaquita 4つの信号を使ってSVを検出
- IMSindel 中間サイズのindelを検出
- Speedseq ヒトゲノムの統合変異検出パイプライン
- Manta 高速なgermlineとsomaticのSV検出ツール
- Scalpel somaticとgermlineのバリアント検出ツール
- CNVkit コピー数変化の検出と可視化ツール
- icopyDAV CNVを検出するパイプライン
- MetaSV 複数のSV検出結果を統合し、精度の高いSVコールを行う
- svviz SVのリードを可視化
- Parliament2 複数のSVコーラーを動かし結果を統合
- SVE Structural Variation Engine
- TankeABreak de brujin graphからinversionを検出
- NucBreak アセンブリの構造的誤りが疑われる部位をコール
- CLOVE SVイベントを統合し、より複雑なSVを予測
- CLEVER 中間サイズのSVを検出
ロングリード
- picky ロングリードを使ってSVを検出
- rMETL ロングリードを使ってMobile elements挿入を検出
- pbsv pacbioのロングリードの構造変異検出
- sniffles ロングリードからSVを検出
- nanoVar ニューラルネットワークを使用したロングリードSVコーラー
- nplnv ロングリードのマッピングから逆位を検出
- cuteSV 高速かつ精度の高いロングリードのSVコーラー (ヒトゲノム)
- SVIM ノイズの多いロングリードを使ってSVをコール
ゲノム比較
- SyRI ゲノムを比較してstructural rearrangementsを検出
- Assemblytics アセンブルをリファレンスと比較してSVを可視化
- Nucdiff ゲノムなどの長い配列同士を比較し、違いをレポート
- paftools PAFファイルを扱うユーティリティ minimap2と連携させてSVのコールも可能
- SVIM-asm De novoアセンブリを直接リファレンスと比較してSVコール(2倍体ゲノムのハプロタイプ解像アセンブリにも対応)
SVの視覚化
- Ribbon SVのリードアライメントやゲノム比較結果を可視化
- samplot 構造変異が起きた部位のマッピング状況を出力
- SplitThreaer リアレンジメントなどのSVを可視化
- Svpluscnv 複雑な構造多型の分析と視覚化を行う
SVのマージ
- FusorSV 複数のSVコール結果をマージ
- SURVIVOR SVシミュレーションやマージ、レポート生成
SVのフィルタリング
- smoove ノイズを除去しながらcohortsのgenotypingを行う
- duphold DupとdelのSVコールから偽陽性コールをフィルタリング
SVのシミュレータ
- simuG 変異が導入されたゲノムをシミュレート
- SURVIVOR SVシミュレーションやマージ、レポート生成
Genotyping
- SV2 SVの正確なGenotypingを行う
- svtyper SVのgenotypingを行う
- smoove ノイズを除去しながらcohortsのgenotypingを行う
- SVJedi VCFのSVコールをロングリードでジェノタイピング
--準備--
homebrewを使って導入するなら、はじめにbrew tap でscience系のコマンドをオフィシャルコマンドとしてインストールできるようにしておく(2018 2/3修正)。
brew tap brewsci/science
ほとんどのスクリプトはインプットとしてソート済みのbamファイルを使う。このbamの作成については、small indelとSNV検出編を確認してください。SNVとsmall indel検出前にbamのリアライメントとBQSR補正を行い、できる限り正確なアライメントを行ったbamを出力する流れを書いています。
R1.fqとR2.fqがfastqファイルで、ref.faがリファレンスとする。
リファレンスのindexも必要とするものが多い。samtools faidxでfasta.faiを作っておく。
samtools faidx $f
これらの結果を1つのフォルダにまとめておき、各スクリプト実行時にそのフォルダを参照するようにする。
--bamの作成、リアライメント、フィルタリング--
bamの作成方法の例を示す。2015のvariant caller比較の論文で使われている方法になる(リンク)。
#1 mapping
#リンク先の論文ではmapperもいくつか紹介されているが、bwa memを使う
bwa mem -t 10 hg19.fa read_1_filtered.fastq read_2_filtered.fastq > ALN.sam
#2 bam変換
samtools view -bS ALN.sam -o ALN.bam
#3 picardでcoordinateソート
picard SortSam VALIDATION_STRINGENCY=SILENT I=ALN.bam \
OUTPUT=ALN_sorted.bam SORT_ORDER=coordinate
#4 depth of coverage計算(bedは各exomeキャプチャのHPからダウンロード)
picard CalculateHsMetrics I=ALN_sorted.bam O=ALN.O.log R=hg19.fa \
TI=truseq_exome.bed BI=genome/truseq_exome.bed \
VALIDATION_STRINGENCY=SILENT PER_TARGET_COVERAGE=ALN.ptc.bed
#5 PCR duplicateを除去
picard MarkDuplicates VALIDATION_STRINGENCY=SILENT I=ALN.sorted.bam \
O=ALN.dups_removed.bam REMOVE_DUPLICATES=true \
M=alignments/metrics
#6 Read Group追加
picard AddOrReplaceReadGroups VALIDATION_STRINGENCY=SILENT \
I=ALN.dups_removed.bam O=ALN.RG.bam SO=coordinate RGID=sample1 \
RGLB=sample1 RGPL=illumina RGPU=sample1 RGSM=sample1 CREATE_INDEX=true
#7 realignment step1
gatk -T RealignerTargetCreator -R hg19.fa -I ALN.RG.bam \
-known mills.vcf -o ALN.intervals
#8 realignment step2
gatk -T IndelRealigner -R hg19.fa -I ALN.RG.bam \
-known mills.vcf -o ALN.indels.bam –maxReadsForRealignment 100000 \
–maxReadsInMemory 1000000 -targetIntervals ALN.intervals
#9 Base recalibration step1(dbSNPの既知変異はfalseではないので計算から除外)
gatk -T BaseRecalibrator -R hg19.fa -I ALN.indels.bam \
-dbsnp_137.hg19.excluding_sites_after_129.only_standard_chroms.vcf \
-o ALN.grp
#10 Base recalibration step2
gatk -T PrintReads -R hg19.fa -I ALN.indels.bam \
-BQSR ALN.grp -o ALN.BQSR.bam
#11 index
samtools index ALN.BQSR.bam
ALN.BQSR.bamとその.baiファイルが得られる。これをSV callerの入力に使う。
--分類--
ショートリードから構造変化を予測する手法は大きく4つに分けることができる。
1、Alignment based
Dindel
Stampy
SAMtools
GATK
Varscan
2、Split-read mapping
Pindel
SV-M
3、Paired-end mapping
Hydra
PEMer
Breakdancer
4、haplotype-based
GATK-HaplotypeCaller
Platypus
--SVを検出するツールの紹介及びランの仕方--
Breakdancer Chen et al. (2009)
discordant paired read approaches
breakdancerのようなread pairの手法はインサートサイズのずれリードの向き(正常なら--> <--)からindelを予測する。つまり、ペアリードのインサートサイズが一般的な正規分布に従うと仮定し、ペア間の距離が分布の外れ値になるような部位にindelがあり、リードの向きがおかしくなる(--> -->や<-- <--)部位にインバーションがあるだろうと考える方法論である。Breakdancerはこのような異常なペアリード; discordant paired read(DPR)情報に基づき構造変化を予測する。ただし、アライメントのエラーもありうるので、エラーを考量して異常なペアが1箇所に2組以上集積している部位をコールしている。
ただしこの手法には大きな問題点がある。まずペア間の距離が大きく変わっていることが前提なのでsmall indelは検出できない。また、インサートサイズの分布によって感度が変化する。さらに構造変化後の配列に関する情報も得られないこともデメリットとなる。
そのため現在ではread pairの手法で構造変化に関する手がかりを掴み、それをsplit-mappingやlocal de novo assemblyを組み合わせて検出する手法がいくつか報告されている。
2017年現在Breakdancer-maxがダウンロードできるが、cpanでたくさんのperlモジュールをインストールする必要があって面倒だった。
--------追記--------
Anaconda環境ならcondaで導入可能
conda install -c bioconda breakdancer
dockerイメージもいくつかあり: 例えば "docker pull molecular breakdancer")。
---------------------
> breakdancer-max
$ breakdancer-max
breakdancer-max version unstable (commit nogit)
Usage: breakdancer-max <analysis.config>
Options:
-o STRING operate on a single chromosome [all chromosome]
-s INT minimum length of a region [7]
-c INT cutoff in unit of standard deviation [3]
-m INT maximum SV size [1000000000]
-q INT minimum alternative mapping quality [35]
-r INT minimum number of read pairs required to establish a connection [2]
-x INT maximum threshold of haploid sequence coverage for regions to be ignored [1000]
-b INT buffer size for building connection [100]
-t only detect transchromosomal rearrangement, by default off
-d STRING prefix of fastq files that SV supporting reads will be saved by library
-g STRING dump SVs and supporting reads in BED format for GBrowse
-l analyze Illumina long insert (mate-pair) library
-a print out copy number and support reads per library rather than per bam, by default off
-h print out Allele Frequency column, by default off
-y INT output score filter [30]
> docker run --rm -it molecular/breakdancer bam2cfg.pl #dockerイメージからrunした
docker run --rm -it molecular/breakdancer bam2cfg.pl
Usage: bam2cfg.pl <bam files>
Options:
-q INT Minimum mapping quality [35]
-m Using mapping quality instead of alternative mapping quality
-s Minimal mean insert size [50]
-C Change default system from Illumina to SOLiD
-c FLOAT Cutoff in unit of standard deviation [4]
-n INT Number of observation required to estimate mean and s.d. insert size [10000]
-v FLOAT Cutoff on coefficients of variation [1]
-f STRING A two column tab-delimited text file (RG, LIB) specify the RG=>LIB mapping, useful when BAM header is incomplete
-b INT Number of bins in the histogram [50]
-g Output mapping flag distribution
-h Plot insert size histogram for each BAM library
——
解析手順は、まずbamファイルをサンプリングしてインサートサイズなどを分析したファイル(.cfgファイル)を作り、それからコールを行う。
#cfgファイルを作成する(orted.bamはbwa memで作成した)。
perl bam2cfg.pl R1R2_sorted.bam > output.cfg
cfgファイルの中身は以下のようになっていた
>cat output.cfg
readgroup:X platform:ILLUMINA map:R1R2_sorted.bam readlen:296.80 lib:Y num:9990 lower:48.86 upper:29146.26 mean:444.35 std:3920.08 SWnormality:minus infinity exe:samtools view
サンプリング自体は最初の数百行だけ行うらしく、すぐに終わる。ただしこの時qualityがpoorなデータだと解析できない (ランした時にpoor quality dataと出る)。 どうしてもランしたければ、オプション"-v"をdefaultの1から2-10まであげると一応ランはできる。
#SVのコール
breakdancer-max output.cfg > breakdancer_output
人のchr20で試すと解析は10分で終わり、500箇所ほどコールされた。
Pindel Ye et al. (2009)
split-read approaches.
ショートリードのペアードエンドデータからdeletion(1bp-10kb)、medium insertion (1-20bp)を予測するツール。リードを分割してアライメントし、そのアライメントのパターンから構造変化を予測している。このようなアライメントをスプリットアライメントと呼び、BWA MEMやRNA-seqで使うtophatなども使っている方式となる。
手法の詳細は論文に書いてあるが、split-read mappingの代表的な論文なのでもう少し手順を説明する。
1、ペアリードの片側だけマップされるペアを探索する。この片側のリードのアライメントが肝なので、ユニークでかつミスマッチがないパーフェクトマッチのアライメントが行われる。
2、相方リードがマップされないのは、この相方リードが構造変化部位を横断するようにマップされているからと考える。この相方リードのアライメント部位を探すため、アライメントできた方のリード(アンカーと呼んでいる)からインサートサイズ平均の2倍の範囲内でマッピングされなかったリードの方がマッチする部位を探す。ただし相方リードはそのままではアライメントできないので、リードを5'側と3'側、真ん中の3ピースに分けてそれぞれでアライメントを実行する(split alignmnet)。
3、5'側と3'側のアライメント部位にずれがあれば、即ちそのずれのサイズがdeletionのサイズになる(下図a)。5'側と3'側のアライメント部位にズレはないが、真ん中のピースが浮いた状態でマッピングされていれば、その真ん中のピースがinsert配列そのもののはずである。
4、2つ以上のペアで同じ情報が検出された部位をコールする。

片方のリードを正確にアライメントし、その相方の位置も限定することで偽陽性を抑え且つ解析をスピードアップしている。原理上リードの長さによって検出可能なindelの長さの上限が決まる。初期の30-40bpのリードでは20bpのinsertionが上限ということらしい。
以下の図は解析の流れ。

http://gmt.genome.wustl.edu/packages/pindel/install.html にインストールの仕方が書いてある。macOSX環境ではインストールできなかったのでcentOSにインストールした。
git clone git://github.com/genome/pindel.git
cd pindel
./INSTALL /path/to/samtools_FOLDER/
--------追記--------
またはconda(linux only)かdocker imagesを使う。
#condaを使う(link)
conda install -c bioconda -y pindel
#dockerイメージも上がっている
docker pull opengenomics/pindel
---------------------
デモランは以下の通りに行う。
cd demo
./pindel -f simulated_reference.fa -i simulated_config.txt -o output
ランに必要なものはリファンレス配列(.fasta)とそのindexファイル(.fasta.fai)。またそのリファレンスにmapして作ったbamファイルとそのindexファイル(.bam.bai)。このあたりは他のツールと変わらない。
pindelは情報を記載したコンフィグファイルを作って、それを元にランする。サンプルファイルたと、コンフィグファイルに相当するのはsimulated_config.txtファイルとなる。ファイル内には以下のことが書かれている(コピペして使うなら、スペース2つなど入れてるので、タブ1つに置換して下さい)。
simulated_sample_1.bam 250 SAMPLE1
simulated_sample_2.bam 250 SAMPLE2
simulated_sample_3.bam 250 SAMPLE3
データが1つなのでこれを以下のように変更した。
R1R2_sorted.bam 600 SAMPLE1
この600はインサートサイズ。ランするには
./pindel -f input.fasta -T 12 -i config.txt -o output
-T: thread
-f: ref.fa
-i: config_file
-o: output
終わると構造変化の種類ごとにアライメントファイルが出力される。結果を見るにはpindel2vcfで変換する。pindel2vcfはビルドしてでできたpindel/に入っている。
pindel2vcf -p output_D -r ref.fa -R ref -d 20170509 -v pindel_output_D.vcf -e 5
pindel2vcf -p output_final -r ref.fa -R ref -d 20170509 -v pindel_INT_final.vcf -e 5
pindel2vcf -p pindel_INV -r ref.fa -R ref -d 20170509 -v pindel_output_INV.vcf -e 5
pindel2vcf -p pindel_SI -r ref.fa -R ref -d 20170509 -v pindel_output_SI.vcf -e 5
pindel2vcf -p pindel_TD -r ref.fa -R ref -d 20170509 -v pindel_output_TD.vcf -e 5
pindel2vcf -p pindel_BP -r ref.fa -R ref -d 20170509 -v pindel_output_BP.vcf -e 5
pindel2vcf -p pindel_LI -r ref.fa -R ref -d 20170509 -v pindel_output_LI.vcf -e 5
-r/--reference The name of the file containing the reference genome: required parameter -R/--reference_name The name and version of the reference genome: required parameter -d/--reference_date The date of the version of the reference genome used: required parameter -p/--pindel_output The name of the pindel output file containing the SVs
-e/--min_supporting_reads The minimum number of supporting reads required for an event to be reported (default 1)
出力のvcfフォーマットはvcf higher versionに準拠しているらしい。
-eは必須パラメータではないが、デフォルトの1では高感度すぎて明確な変異なしのシミュレートデータ(50カバレッジ)でも1000近くの偽陽性コールが検出される。indelソフトのパフォーマンス比較の論文で-e 5になっていたのでここではそれに習った。ただし、目的やリードのカバレッジによってチューニングが必要と思われる。略語は以下のように説明されている。
D = deletion
SI = short insertion
INV = inversion
TD = tandem duplication
LI = large insertion
BP = unassigned breakpoints
最終的には以下のようなフローで全タイプのSVを検出できる。
pindel -f input.fasta -T 12 -i config.txt -o pindel
cat pindel_SI pindel_D pindel_LI pindel_TD > pindel.txt
pindel2vcf -R input.fasta -r input.fa -p pindel.txt -v pindel.vcf -d 20171019 -e 5
vcffilter -f " SVTYPE = INS | SVTYPE = DEL " pindel.vcf > pindel.indel.vcf
vcffilterがないなら、vcftlibsのレポジトリを--recursiveをつけてクローンする。
> git clone https://github.com/vcflib/vcflib.git --recursive
> cd vcflib/ && make && cd bin/
> ./vcffilter
> #たくさんツールがある。ここではディレクトリ全体にパスを通す。
> echo 'export PATH=$PATH:`pwd`' >> ~/.bash_profile && source ~/.bash_profile
GASVpro Sindi et al. (2012)
discordant paired read approaches
インストールは、解凍したディレクトリの中で以下のコマンドを打つだけでよい。
./install
入力はbamファイルとなる。ランは2段階で行う。
java -Xms512m -Xmx2048m -jar BAMToGASV.jar R1R2_sorted.bam -MAPPING_QUALITY 30 -CUTOFF_LMINLMAX SD=3
-MAPPING_QUALITY:
-CUTOFF_LMINLMAX:
LUMPY layer et al. (2014)
split-read + discordant paired read + CNV based approaches.
解析の流れはこのURLに丁寧に書いてある。
macOSX環境でのインストールも可能。homebrewでインストールできる。
brew install homebrew/science/lumpy-sv
#Bioconda (link)
conda install -c bioconda -y lumpy-sv
#docker images (非オフィシャルだが動作確認済み)
docker pull erictdawson/lumpy-sv
ソフトクリップのマッピングファイルから構造変化を予測する手法。マッピングソフトは1Mbpまで対応したbwa memなどのマッパーを使う。デプスのないデータなどでもsensitivityが高いらしい。また複数サンプルで差分をとって精度を上げるやり方も搭載している。
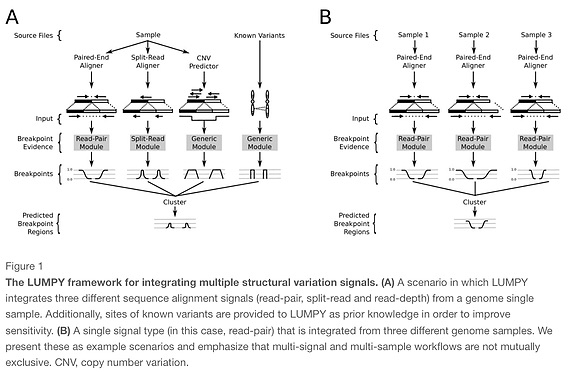
テストランはtestディレクトリにあるtest.shを実行する。
./test.sh
問題なければNA12878、honeybee、riceのindel予測結果がvcf形式で出力される。
解析時は下のような流れでコールする。
bwa index -a bwtsw ref.fa
bwa mem -R "@RG ID:X LB:Y SM:Z PL:ILLUMINA" ref.fa R1.fastq R2.fastq |samtools view -S -b - > sample.bam
samtools view -@ 12 -b -F 1294 sample.bam > sample.discordants.unsorted.bam
samtools view -@ 12 -h sample.bam | extractSplitReads_BwaMem -i stdin | samtools view -@ 12 -Sb - > sample.splitters.unsorted.bam
samtools sort -@ 12 sample.discordants.unsorted.bam > sample.discordants.bam
samtools sort -@ 12 sample.splitters.unsorted.bam > sample.splitters.bam
#準備できたらlumpyのコマンドを走らせる
lumpyexpress -B sample.bam -S sample.splitters.bam -D sample.discordants.bam -o sample.vcf
解析できるまで手間取った。最後の肝心のlumpyexpressがモジュールを読み込めずエラーになる。最終的に強引にrootで進めることでなんとかランできた。
samtoolsのソートでエラーになる人は、>(リダイレクト)とリダイレクトの後ろ側の.bamを決してランする。これはsamtoolsのバージョンによっては>と.bamが入らないバージョンがあるため。
追記
上の図に載っているように複数サンプルの差分や同時解析もできる。
1、normalサンプルについて上のコマンドを実行し、SVに関係するリードのbamを得る。
2、tumorサンプルについて上のコマンドを実行し、SVに関係するリードのbamを得る。
3、lumpyで解析
#1 normal sample
bwa mem -R "@RG\tID:X\tLB:Y\tSM:normal\tPL:ILLUMINA" -t 12 ref.fa normalpair1.fq normalpair2.fq |samtools view -@ 12 -S -b - > normal.bam
samtools view -@ 12 -b -F 1294 normal.bam > normal.discordants.unsorted.bam
samtools view -@ 12 -h normal.bam | extractSplitReads_BwaMem -i stdin | samtools view -@ 12 -Sb - > normal.splitters.unsorted.bam
samtools sort -@ 12 normal.discordants.unsorted.bam > normal.discordants.bam
samtools sort -@ 12 normal.splitters.unsorted.bam > normal.splitters.bam
#2 tumor sample
bwa mem -R "@RG\tID:X\tLB:Y\tSM:tumor\tPL:ILLUMINA" -t 12 ref.fa tumor_pair1.fq tumor_pair2.fq |samtools view -@ 12 -S -b - > tumor.bam
samtools view -@ 12 -b -F 1294 tumor.bam > tumor.discordants.unsorted.bam
samtools view -@ 12 -h tumor.bam | extractSplitReads_BwaMem -i stdin | samtools view -@ 12 -Sb - > tumor.splitters.unsorted.bam
samtools sort -@ 12 tumor.discordants.unsorted.bam > tumor.discordants.bam
samtools sort -@ 12 tumor.splitters.unsorted.bam > tumor.splitters.bam
#3 turmor-normal call (case - control)
lumpyexpress \
-B tumor.bam,normal.bam \
-S tumor.splitters.bam,normal.splitters.bam \
-D tumor.discordants.bam,normal.discordants.bam \
-o tumor_normal.vcf
#multiple samplesの場合
lumpyexpress \
-B sample1.bam,sample2.bam,sample3.bam \
-S sample1.splitters.bam,sample2.splitters.bam,sample3.splitters.bam \
-D sample1.discordants.bam,sample2.discordants.bam,sample3.discordants.bam \
-o multi_sample.vcf
lumpyはspeedseqパイプラインでも使われています。動作も高速で(bamを順次作っていく流れが1コマンドでできる(speedseq aln))、他のツールの結果もまとめてくれます。speedseqも検討してみてください(リンク)。
Hydra-sv
discordant paired read approaches.
マニュアル: Google Code Archive - Long-term storage for Google Code Project Hosting.
下のような流れでコールする。(https://code.google.com/archive/p/hydra-sv/wikis/TypicalWorkflow.wiki)
bwa index -p $f -a is $f
bwa aln -t 12 $f $p > R1.sai
bwa aln -t 12 $f $q > R2.sai
bwa sampe $f R1.sai R2.sai $p $q |samtools view -Sb - > sample.tier1.queryorder.bam
samtools view -uF 2 sample.tier1.queryorder.bam |bamToFastq -bam stdin -fq1 R1_disc1.fq -fq2 R2_disc1.fq
novoindex ssuis.nix $f #Novoalignのindex
novoalign -d ssuis.nix -f R1_disc1.fq R2_disc1.fq -i 500 50 -r Random -o SAM |samtools view -Sb - > sample.tier2.queryorder.bam
samtools view -uF 2 sample.tier2.queryorder.bam |bamToFastq -bam stdin -fq1 R1_disc2.fq -fq2 R2_disc2.fq
novoalign -d ssuis.nix -f R1_disc2.fq R2_disc2.fq -i 500 50 -r Ex 1100 -t 300 -o SAM |samtools view -Sb - > sample.tier3.queryorder.bam
bamToBed -i sample.tier3.queryorder.bam -tag NM |pairDiscordants.py -i stdin -m hydra -z 800 > sample.disc.bedpe
dedupDiscordants.py -i sample.disc.bedpe -s 3 > sample.disc.deduped.bedpe
hydra -in sample.disc.deduped.bedpe -out sample.breaks -mld 500 -mno 1500
ただし結果はひどくしょぼい。進め方かパラメータを間違ってる可能性がある。
DELLY2 Rausch et al. (2012)
split-read +discordant paired read approaches.
Delly2 can discover,deletions, tandem duplications, inversions and translocations at single-nucleotide resolution in short-read massively parallel sequencing data.
deletionなどを予測する。コピーナンバーが変わるリピートのdeletionや、depthが少ないデータにも強いらしい。 コントロールのデータ(somatic sampleなど)と解析データ(tumor sampleなど)両方を使った差分解析を特徴とするが、単体のデータでも解析は可能。insertionはターゲットではないので注意する。こちらからダウンロードできる。
centOSサーバーにインストールした。
基本的にはgitからダウンロードしてmakeするだけ。
git clone --recursive https://github.com/dellytools/delly.git
cd delly/
make all
#bioconda
conda install -c bioconda -y delly
brewで入れるとversion 0.7.7が入る。mac osにも導入可能。
$ delly
**********************************************************************
Program: Delly
This is free software, and you are welcome to redistribute it under
certain conditions (GPL); for license details use '-l'.
This program comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY; for details use '-w'.
Delly (Version: 0.7.7)
Contact: Tobias Rausch (rausch@embl.de)
**********************************************************************
Usage: delly <command> <arguments>
Commands:
call discover and genotype structural variants
merge merge structural variants across VCF/BCF files and within a single VCF/BCF file
filter filter somatic or germline structural variants
ランは
./delly call -t DEL -x human.hg19.excl.tsv -o delly.bcf -g ref.fa R1R2_sorted.bam
-xはなくても問題ないが、コールを除外する領域を設定できる(例えばヒトのセントロメアなど)。
コントロールと比較するなら
./delly call -t DEL -x human.hg19.excl.tsv -o delly.bcf -g ref.fa R1R2_sorted.bam Control_R1R2_sorted.bam
Contorl~bamは変異がないと期待される体細胞シーケンスデータ。tumor~bamが変異の可能性がある腫瘍組織のシーケンスデータ。
ランが終わるとbinaryのbcfファイルが出力される。結果を見るにはbedtoolsで変換する必要がある。
./bcftools/bcftools view delly.bcf > delly.vcf
この時フィルターコマンドは実行することも可能。
5つのコールタイプがあるので逐一実行する。
./delly call -t DEL -o del.bcf -g ref.fa R1R2_sorted.bam &
./delly call -t DUP -o dup.bcf -g ref.fa R1R2_sorted.bam &
./delly call -t INV -o inv.bcf -g ref.fa R1R2_sorted.bam &
./delly call -t TRA -o tra.bcf -g ref.fa R1R2_sorted.bam &
./delly call -t INS -o ins.bcf -g ref.fa R1R2_sorted.bam &
./bcftools/bcftools view del.bcf > deletions.vcf
./bcftools/bcftools view dup.bcf > duplications.vcf
./bcftools/bcftools view inv.bcf > inversions.vcf
./bcftools/bcftools view tra.bcf > translocations.vcf
./bcftools/bcftools view ins.bcf > insertions.vcf
Platypus Rimmer et al. (2014)
local assembly based approaches.
nature geneticsに載った手法。原理の詳細はこちら http://nextgenseek.com/2014/07/platypus-a-new-variant-caller-that-integrates-mapping-assembly-and-haplotype-based-approaches/
候補部位をローカルリアライメントしてプロタイプを調べ、さらにlocal de novo assemblyも行いSNV、indel、complex polumorphismsを検出する手法。パフォーマンス比較の論文でも精度が高いと評価されている。
ふつうショートリードのアライメントは各々の塩基が一致するかに焦点を当てて行われる。この方式は計算リソースの面から考えると大量のデータを処理するには向いているが、indel周辺はミスマッチが多発してしまうことになる。そこでindelを考量して計算リソースを潤沢に使った丁寧なギャップアライメントを行う機能がいくつかの手法に実装されている(GATKなど)。ただしギャップアライメントでうまく補正できるのはせいぜい数塩基で、long indelが起きていた場合修正しきれない。Platypusはそのような補正が出来ない領域だけを対象にde novoでアセンブルを行い、long indelの検出を試みる手法である。対象領域を限定することで、解析スピードを大きく縮小していることも特徴の1つで、例えば数メガのバクテリアの解析だと早ければ1分以内でランは終わる。
2021/05
platypusは人気のツールであるが、ローカルアセンブリをするかどうかの切り替えの問題で精度が劣っているという話もある(Stack exchange)。octopusも確認して下さい。論文でPlatypusやGATK4 、deepvariants、freebayesなどと比較されています。
インストール
mamba create -n platypus python=2 -y
conda activate platypus
mamba install -c bioconda -y platypus-variant
ラン。Coordinate sort済みのbamファイルを使う。
#1サンプル。assembleはオフにすると非常に高速。20コア指定。
platypus callVariants --refFile=ref.fa --bamFiles=sample1.bam --assemble=1 --nCPU=30 -o output.vcf
#multi sample
platypus callVariants --refFile=ref.fa --bamFiles=sample1.bam,sample2.bam,sample3.bam --assemble=1 --nCPU=30 -o output.vcf
--refFile: index付きのfastaファイル
--bamFiles: bamの指定。bamは複数入力可能。その時はbamをコンマで区切る。
パスを通しておけばPlatypus.pyだけで動く。
追記 --assemble=1にしないとランタイムは短くなりますが、local assemblyは実行せず、realignmentだけでindelをコールします(defaultは0)。
デフォルトではサポートするリードが2で検出するため、ディープにシーケンスしたデータでは感度を下げたい場合がある。サポートするリードを4に変えるなら--minReads 4 とする。他にもregionを限定するオプション(--regions)、またVCFファイルを読み込ませて変異をアノテートするオプション(--source)もある(--sourceは試していない)。SNPsはコールしない場合は、--genSNPs=0をつける。--maxSizeはデフォルトでは1500-bpに設定されている。これ以上大きなSVを検出したい場合はサイズをあげる。詳細はHP参照。
複数サンプルのジョイントコールを行うことで、あるサンプルで弱くサポートされているバリアントであっても、他のサンプルで強くサポートされていれば、信頼性をあげてコールすることができる。
解析速度は非常に早く、exomeだと1サンプル1分以内にランは終わった。exome3サンプルの--assemble=1でも、--nCPU=40だと2分で終わった。ヒトWGSの30xでも20分で終わるらしい。
コマンド
http://www.well.ox.ac.uk/platypus-examples
fermikit Li (2015)
assembly based approaches.
一度アセンブルを行なって、それからアライメントをとるプログラム。そう聞くと重そうだが、ヒトゲノムデータでもピークメモリー使用量は90GBくらいで、アセンブルも24時間くらいで終わると書いてある。またその先のアライメントは1時間半くらいで終わるとのこと。
macOSでも動く。インストールは
git clone --recursive https://github.com/lh3/fermikit.git
cd fermikit
make
ビルドしてできたfermi.kitフォルダの中に実行に必要なものが入っている。アライメントにbwaを使っている。
追記
Bioconda
conda install -c bioconda -y fermikit
実行にはリファレンスのbwa indexが必要なので最初に作っておく。
bwa index ref.fa
アセンブル条件ファイルの作成
fermi2.pl unitig -s 3m -t 12 -l 301 -p prefix R1.fastq > prefix.mak
-s: 推定ゲノムサイズ(3mは3 Mbp)
-l: リード長 (Miseq 301bp)
-p 出力されるprefix名
ペアーリードには対応していないみたいで、ペアリード指定の方法が見つからない。
make -f prefix.mak
structural variationsのコール
fermi.kit/run-calling -t 12 ref.fa prefix.mag.gz | sh
prefix.mag.gzとprefix.flt.vcf.gzというファイルができる。READMEには
`prefix.flt.vcf.gz` for filtered SNPs and short INDELs and `prefix.sv.vcf.gz` for long deletions,
に書いてある通り、prefix.flt.vcf.gzの中にSV予測結果、prefix.sv.vcf.gzの中にlong del予測結果が保存されている。playtus同様、解析時間は非常に短い。playtusやfermikitはPEM法などで予測が難しいsmall indelもコールしてくれるのが1つの利点と言える。
追記1; 70bp以下のリードだと動作しない。BBtoolsでペアリードをマージしてみると使えるかもしれない。
#ペアリードをマージする。マージできなかった場合、k=20merで5回伸長してマージする。
bbmerge-auto.sh in1=inputR1.fastq in2=inputR2.fastq out=merged.fq outu=unmerged.fq ihist=ihist.txt ecct extend2=20 iterations=5
#seqkitで平均長を調べる
seqkit stats merged.fq
平均長を使いfermikitラン。
BBtoolは別に紹介しています(リンク)。
追記2; ゲノムサイズやリード長を正しく記載しないと上手くSV検出できない。リード長の平均がわからなければ、seqkit stats input.fastqなどでaverageを調べてから使ってみてください。
FreeBayes Garrison and Marth (2012)
gapped alignment approaches.
macOSでも動く。SNVと小さなindeを検出できる。ベイズ的アプローチでバリアントを検出する。 ヒトゲノム解析でhaplotypeの変異を検出するために開発された。倍数体ゲノムの変異検出やpooledサンプル(複数ゲノムのmixture)にも対応している(公式参照)。
brewかcondaでインストール可能。
#homebrew
brew install FreeBayes
#bioconda
conda install -c bioconda -y FreeBayes
freebayes -f ref.fa -b R1R2_sorted.bam > out.vcf
感度は-Cで調整できる。デフォルトの"-C 2"では感度が高すぎて、例えば50リードシーケンスリードがある部位で2リードだけッミスマッチがあると検出される。腫瘍の変異などわずかな変異を検出するには都合良いが、この条件では偽陽性も大量に出てくるので、サンプルによっては調整が必要(-Cオプションとか)。
追記
Variant callの論文(リンク)では、以下のようなコマンドで実行している。
#SNVs
freebayes -f hg19.fa -i -X -u -v vcf_freebayes.raw.snv.vcf NA12878.ALIGNER.BQSR.bam
#indel
freebayes -f hg19.fa -I -X -u -v freebayes.raw.indel.vcf NA12878.ALIGNER.BQSR.bam
- -X --no-mnps Ignore multi-nuceotide polymorphisms, MNPs.
- -u --no-complex Ignore complex events (composites of other classes).
- -v --vcf Output VCF-format results to FILE. (default: stdout)
- -i --no-indels Ignore insertion and deletion alleles.
- -I --no-snps Ignore SNP alleles.
GATK
split-read approaches.
多分一番有名な有名なツール。 https://software.broadinstitute.org/gatk/documentation/topic?name=methods に詳細が記載されている。best practic絵のペーパーが出ているので、それを読んで勉強した方がよい。よいツールだが、関連項目が多く学習曲線は長め。
UnifiedGenotyperのラン
gatk -T UnifiedGenotyper -R ref.fa -I R1R2_sorted.bam -o UnifiedGenotyper.txt
HaplotypeCallerのラン
gatk -T HaplotypeCaller -R ref.fa -I R1R2_sorted.bam -o HaplotypeCaller.txt
SvABA Wala et al. (2017)
local assembly approaches.
macでもインストール可能とあったが、ビルド中にエラーが出たのでcentOSにインストールした。
git clone --recursive https://github.com/walaj/svaba
cd svaba
./configure
make
make install
#bioconda
conda install -c bioconda -y svaba
ビルドが終わると、src/svaba/に実行ファイルのバイナリができる。
$ svaba run
Usage: svaba run -t <BAM/SAM/CRAM> -G <reference> -a myid [OPTIONS]
Description: SV and indel detection using rolling SGA assembly and BWA-MEM realignment
General options
-v, --verbose Select verbosity level (0-4). Default: 0
-h, --help Display this help and exit
-p, --threads Use NUM threads to run svaba. Default: 1
-a, --id-string String specifying the analysis ID to be used as part of ID common.
Main input
-G, --reference-genome Path to indexed reference genome to be used by BWA-MEM.
-t, --case-bam Case BAM/CRAM/SAM file (eg tumor). Can input multiple.
-n, --control-bam (optional) Control BAM/CRAM/SAM file (eg normal). Can input multiple.
-k, --region Run on targeted intervals. Accepts BED file or Samtools-style string
--germline Sets recommended settings for case-only analysis (eg germline). (-I, -L5, assembles NM >= 3 reads)
Variant filtering and classification
--lod LOD cutoff to classify indel as non-REF (tests AF=0 vs AF=MaxLikelihood(AF)) [8]
--lod-dbsnp LOD cutoff to classify indel as non-REF (tests AF=0 vs AF=MaxLikelihood(AF)) at DBSnp indel site [5]
--lod-somatic LOD cutoff to classify indel as somatic (tests AF=0 in normal vs AF=ML(0.5)) [2.5]
--lod-somatic-dbsnp LOD cutoff to classify indel as somatic (tests AF=0 in normal vs AF=ML(0.5)) at DBSnp indel site [4]
--scale-errors Scale the priors that a site is artifact at given repeat count. 0 means assume low (const) error rate [1]
Additional options
-L, --mate-lookup-min Minimum number of somatic reads required to attempt mate-region lookup [3]
-s, --disc-sd-cutoff Number of standard deviations of calculated insert-size distribution to consider discordant. [3.92]
-c, --chunk-size Size of a local assembly window (in bp). Set 0 for whole-BAM in one assembly. [25000]
-x, --max-reads Max total read count to read in from assembly region. Set 0 to turn off. [50000]
-C, --max-coverage Max read coverage to send to assembler (per BAM). Subsample reads if exceeded. [500]
--no-interchrom-lookup Skip mate lookup for inter-chr candidate events. Reduces power for translocations but less I/O.
--discordant-only Only run the discordant read clustering module, skip assembly.
--num-assembly-rounds Run assembler multiple times. > 1 will bootstrap the assembly. [2]
--num-to-sample When learning about inputs, number of reads to sample. [2,000,000]
--hp Highly parallel. Don't write output until completely done. More memory, but avoids all thread-locks.
Output options
-z, --g-zip Gzip and tabix the output VCF files. [off]
-A, --all-contigs Output all contigs that were assembled, regardless of mapping or length. [off]
--read-tracking Track supporting reads by qname. Increases file sizes. [off]
--write-extracted-reads For the case BAM, write reads sent to assembly to a BAM file. [off]
Optional external database
-D, --dbsnp-vcf DBsnp database (VCF) to compare indels against
-B, --blacklist BED-file with blacklisted regions to not extract any reads from.
-Y, --microbial-genome Path to indexed reference genome of microbial sequences to be used by BWA-MEM to filter reads.
-V, --germline-sv-database BED file containing sites of known germline SVs. Used as additional filter for somatic SV detection
-R, --simple-seq-database BED file containing sites of simple DNA that can confuse the contig re-alignment.
Assembly and EC params
-m, --min-overlap Minimum read overlap, an SGA parameter. Default: 0.4* readlength
-e, --error-rate Fractional difference two reads can have to overlap. See SGA. 0 is fast, but requires error correcting. [0]
-K, --ec-correct-type (f) Fermi-kit BFC correction, (s) Kmer-correction from SGA, (0) no correction (then suggest non-zero -e) [f]
-E, --ec-subsample Learn from fraction of non-weird reads during error-correction. Lower number = faster compute [0.5]
--write-asqg Output an ASQG graph file for each assembly window.
BWA-MEM alignment params
--bwa-match-score Set the BWA-MEM match score. BWA-MEM -A [2]
--gap-open-penalty Set the BWA-MEM gap open penalty for contig to genome alignments. BWA-MEM -O [32]
--gap-extension-penalty Set the BWA-MEM gap extension penalty for contig to genome alignments. BWA-MEM -E [1]
--mismatch-penalty Set the BWA-MEM mismatch penalty for contig to genome alignments. BWA-MEM -b [18]
--bandwidth Set the BWA-MEM SW alignment bandwidth for contig to genome alignments. BWA-MEM -w [1000]
--z-dropoff Set the BWA-MEM SW alignment Z-dropoff for contig to genome alignments. BWA-MEM -d [100]
--reseed-trigger Set the BWA-MEM reseed trigger for reseeding mems for contig to genome alignments. BWA-MEM -r [1.5]
--penalty-clip-3 Set the BWA-MEM penalty for 3' clipping. [5]
--penalty-clip-5 Set the BWA-MEM penalty for 5' clipping. [5]
ランは
svaba run -p 12 -t R1R2_sorted.bam -G re.fa
-t: bamファイル。
-G: リファレンス。
~indel.vcfが出力ファイル。
-p: thread数
bedファイルを指定することで解析領域を限定することも可能。マニュアルには300bpまでのinsertionをコールできるとあるが、検証したところ確かに300bpまでの長さのInsertionを検出できていた。
VarScan Koboldt et al. (2009)
gapped alignment approaches.
BLAT, Newbler, cross_match, Bowtie and Novoalignなどの多くのアライナーをサポートしている。
macOSでも動く。brewやcondaでインストール可能。
#homebrew
brew install VarScan
#Bioconda
conda install -c bioconda -y varscan
Varscanはpileupデータを使うため、初めにソート済みbamファイルをpileupする必要がある。
samtools mpileup -f re.fa R1R2_sorted.bam > mpileup
SNVをコール
VarScan pileup2snp mpileup > output.txt
indelをコール
VarScan pileup2indel mpileup > output.txt
オプションとして以下のようなものがある。
--min-coverage Minimum read depth at a position to make a call [8]
--min-reads2 Minimum supporting reads at a position to call variants [2]
--min-avg-qual Minimum base quality at a position to count a read [15]
--min-var-freq Minimum variant allele frequency threshold [0.01]
--min-freq-for-hom Minimum frequency to call homozygote [0.75]
--p-value Default p-value threshold for calling variants [99e-02]
--variants Report only variant (SNP/indel) positions [0]
pileupしたファイルは大きいので、パイプを使い1ライナースクリプトで進めるやり方がHPに紹介されている。例えばindelをコールするなら
samtools mpileup -f ref.fa R1R2_sorted.bam | VarScan pileup2indel > output.txt
Breseq Deatherage et al. (2014)
split-read approaches.
brew install Breseq
#Anaconda環境なら
conda install -c bioconda -y breseq
#おそらく公式ではないがdockerイメージもある(link)例えば0.32.1タグ
docker pull ummidock/breseq:0.32.1
> breseq
$ breseq
================================================================================
breseq 0.31.1 http://barricklab.org/breseq
Active Developers: Barrick JE, Deatherage DE
Contact: <jeffrey.e.barrick@gmail.com>
breseq is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the
terms the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software
Foundation; either version 2, or (at your option) any later version.
Copyright (c) 2008-2010 Michigan State University
Copyright (c) 2011-2017 The University of Texas at Austin
If you use breseq in your research, please cite:
Deatherage, D.E., Barrick, J.E. (2014) Identification of mutations
in laboratory-evolved microbes from next-generation sequencing
data using breseq. Methods Mol. Biol. 1151: 165–188.
If you use structural variation (junction) predictions, please cite:
Barrick, J.E., Colburn, G., Deatherage D.E., Traverse, C.C.,
Strand, M.D., Borges, J.J., Knoester, D.B., Reba, A., Meyer, A.G.
(2014) Identifying structural variation in haploid microbial genomes
from short-read resequencing data using breseq. BMC Genomics 15:1039.
================================================================================
Usage: breseq -r reference.gbk [-r reference2.gbk ...] reads1.fastq [reads2.fastq.gz ...]
Run the breseq pipeline for predicting mutations from haploid microbial re-sequencing data.
FASTQ read files (which may be gzipped) are input as the last unamed argument(s).
Allowed Options
-h,--help Produce help message showing advanced options
-r,--reference <arg> File containing reference sequences in GenBank, GFF3, or FASTA format. Option may be provided multiple times for multiple files (REQUIRED)
-n,--name <arg> Human-readable name of the analysis run for output (DEFAULT=<none>)
-j,--num-processors <arg> Number of processors to use in multithreaded steps (DEFAULT=1)
-o,--output <arg> Path to breseq output (DEFAULT=.)
-p,--polymorphism-prediction The sample is not clonal. Predict polymorphic (mixed) mutations. Setting this flag changes from CONSENSUS MODE (the default) to POLYMORPHISM MODE
--no-junction-prediction Do not predict new sequence junctions
Utility Command Usage: breseq [command] options ...
Sequence Utility Commands: CONVERT-FASTQ, CONVERT-REFERENCE, GET-SEQUENCE
Breseq Post-Run Commands: BAM2ALN, BAM2COV, CL-TABULATE
For help using a utility command, type: breseq [command]
================================================================================
indelコールは
breseq -r ref.fa -j 12 R1.fq R2.fq -o outdir
-r; リファレンスを指定。fast.gbk (genbank形式)、GFF3に対応。
-j: スレッド数
-0: アウトプット
遺伝子のアノテーションがついたgff3かgenbankファイルがあるなら、検出結果を遺伝子の部位情報付きで出してくれるので非常に便利。genbankファイルは、NCBIのftpサイトか、もしくは該当ページの情報を配列付きで表示させて全テキストコピーしてもいい。gff3ファイルはUCSCなどからダウンロードできる。genbankリファンレスでのランは
breseq -r ref.gbk -j 12 R1.fq R2.fq -o outdir
#dockerイメージ、fastqとGenbankのあるディレクトリで
docker run --rm -u $(id -u):$(id -g) -itv $PWD:/data -w /data \
ummidock/breseq:0.32.1 breseq \
--reference annotation.gbk \
--name sample1 -j 8 --output breseq \
pair1.fq.gz pair2.fq.gz
感度調整のオプションはないが、-pをつけると多型検出ができる。helpのメッセージを載せておく。
-p,--polymorphism-prediction The sample is not clonal. Predict polymorphic (mixed) mutations. Setting this flag changes from CONSENSUS MODE (the default) to POLYMORPHISM MODE
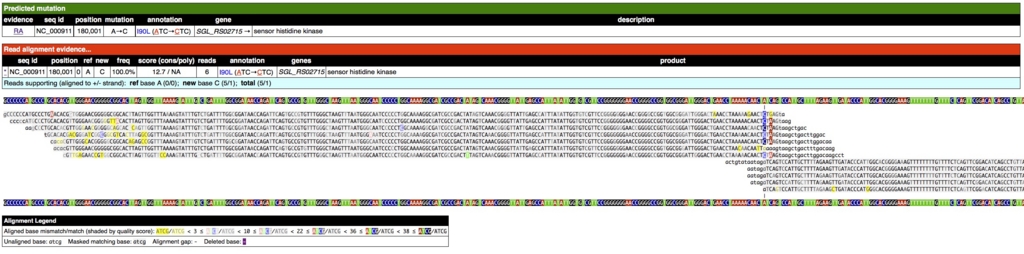
解析が終わるとhtmlのまとめファイルができるのが特徴。内部でRなどの描画ライブラリを動かしているぽい。/outputの中のsummary.htmlを開くと、

上のようにアミノ酸置換まで含めて報告されている。
変異部位をクリックするとアライメント結果も表示される。
coverage
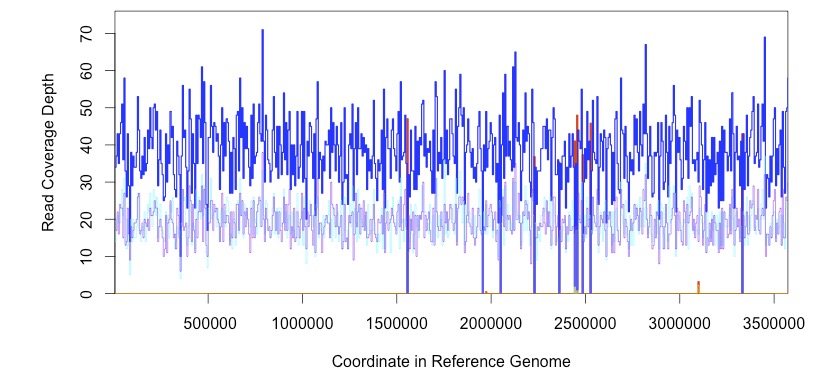
deletion予測時は下のようにリードのデプスを見ることもできる。
indelの抜け漏れはこの中で一番少なかった。インフォマティクスのツールに不慣れなユーザーにも使いやすいと思われる。ただし、動作が複雑なためか他のソフトの安定性かわからないが、時折解析中にエラーを起こす。そうゆう時は大体パラレルにBreseqを動作させていた時だったりする。複数走らせないほうよい。
追記1; バクテリア解析用に設計されており、真核生物ゲノムだとかなり重たい。(100Mbゲノムだと20コア使用で数日かかった)
追記2; vcf出力はdata/output.vcfに出力される。
追記3; 不完全な変異は証拠が不十分になるため、最終出力に残らないことがある。不完全変異も調べるならoutput/output.gdをチェックする。
追記4
breseqだけで完結するように設計されている。そのため人の目で解釈しずらいVCFは出さない。他のツールと連携させる前提なら、VCFなど出さないbreseqはオススメしない。
-pをつけると、クローナルなサンプルのサンプルのバリアント検出から、ミクスチャーのサンプルのバリアントコールに変更できる。おそらく研究室進化などのサンプルで、heterogeneticalなアレルのバリアント検出を行いたい時などにも使うことができる。
追記
Scalpel Narzisi et al. (2014)
assembly based approaches.
ヒトゲノムをターゲットにしている。腫瘍サンプル特異的な変異の差分検出もできる。オプションにもdad(父)とかmam(母)とかある。人のサンプルを使うことがあれば試してみたい。一応ランの流れを書いておく。
#Bioconda
conda install -c bioconda -y scalpel
解析にはbedフォーマットのポジション情報が必要(リンク)。
bcftoolsを使ってbamファイルから変換することができる(SEQanswers)。bamファイルはあらかじめソートしてindexをつけておく。
bamToBed -i R1R2_sorted.bam > R1R2_sorted.bed
Runにはデータベースファイルが必要。
scalpel-discovery --single --bam R1R2_sorted.bam --bed R1R2_sorted.bed --ref ref.fa
上のコマンドを実行するとoutdir/フォルダに色々なファイルができる。その中にvariants.db.dirというファイルができている。これがデータベースファイル。データベースファイルができないエラーもあるらしい。
indelの解析
scalpel-export --single --db outdir/variants.db.dir --bed R1R2_sorted.bed --ref ref.fa
人データでテストしたところ、エラーなく最後まで走ったが、コールがゼロになる。
現在のところ未解決
下にリンクを追加しました。
Breakseek Zhao et al. (2015)
breakpoint + discordant paired read approaches.
pythonで動くため、ソースコードのビルドは必要ないがpython の2.7が必要。
またランにはsamファイルが必要。推奨される作り方がマニュアルに書いてあるのでそれに従う。bwa backtrackを使う。
bwa index -a bwtsw ref.fa
bwa aln ref.fa read1.fq > read1.sai
bwa aln ref.fa read2.fq > read2.sai
bwa sampe ref.fa read1.sai read2.sai read1.fq read2.fq > aln_pe.sam
テスト用のsamとfaが用意されている。下記URLからダウンロードする。
https://sourceforge.net/projects/breakseek/files/toy_testset/
以下はそのファイルで進行している。
bwa alnでsamを作ったら、sam_prep.pyでクロモソームごとに分割する。
python sam_prep.py -f test.sam
終わるとfasta内のクロモソームごとにディレクトリが作られ、中にsamができる。このsamファイルを使ってランする。
python breakseek.py -f testS.sam -m 600 -s 100 -c 50 -q 250 -n 12 -r test.fa
-m: インサートサイズ
-s: インサートサイズのSD。正規分布ならインサートサイズの10-20%くらいらしい。
-c: リードデプス
-q: リード長
以下のメッセージ
gathering statistics on the dataset...
が出てから、解析途中は何もlogが出てこない。初めはランに失敗したと思っていたが、強制終了せず気長に待ったところ、1時間近くかかった。3Mのバクテリアゲノムを使っただけでこれは長い...。プログラムの最適化の度合いが低いのかもしれない。
samファイルはbwa alnでなくてもOK。例えばbwaの別のアルゴリズムbwa memを使うなら
bwa index -a is test.fa
bwa mem -R "@RG ID:X LB:Y SM:Z PL:ILLUMINA" -t 12 test.fa R1.fq R2.fq > R1R2.sam
is: bwaのindexアルゴリズム。"bwasw"か"is"。
-t: スレッド数
R1.fq: fastqファイル
R2.fq: fastqファイル
Scanindel Yang et al. (2015)
gapped alignment + split reads and + assembly based approaches.
performance比較の論文で高評価されているツール。
動作に必要なものがgitのダウンロードページに記載されている。
Softwares and Python packages:
- BedTools/2.17.0 (https://github.com/arq5x/bedtools2/releases)
- SAMtools/1.0 (http://samtools.sourceforge.net/)
- BWA/0.7.10 (http://bio-bwa.sourceforge.net/)
- BLAT (gfServer and gfClient)/34+ (http://genome.ucsc.edu/FAQ/FAQblat.html)
- freebayes/0.9.18 (https://github.com/ekg/freebayes)
- Inchworm assembler (http://inchworm.sourceforge.net)
- Python/2.7 (https://www.python.org/)
- Pysam/0.7.7 (https://code.google.com/p/pysam/)
- PyVCF/0.6.7 (https://github.com/jamescasbon/PyVCF)
- Biopython/1.64 (http://biopython.org/wiki/Main_Page)
- SciPy/0.14.0 and NumPy/1.8.1 (http://www.scipy.org/)
Anaconda環境なら以下のコマンドでワンライナーインストールできる(bioconda)。
conda install -c bioconda scanindel
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
インストール当時はcondaに頼らず導入した。
上の依存の大半はbrewとpipコマンドですぐ導入できたが、Inchwormはmacで動作しなかった。最終的にubuntu 14.04にインストールした。まずbrewで導入できるコマンドでないものがあれば入れておく。
brew listでインストール済みリストのチェック。
brew list
下のコマンドのうちlistででないものがあれば導入。
brew install bwa
brew install samtools
brew install bedtools
brew install blat
brew install freebayes
pysam、PyVCF、Biopython、SciPy、NumPyもpythonのpipコマンドで導入できる。PyVCFはpythonのSNV検出スクリプト。
インストールされているpythonライブラリの確認
pip freeze
ないものがあれば導入。
pip install pysam
pip install PyVCF
pip install Biopython
pip install --user numpy scipy matplotlib ipython jupyter pandas sympy nose
Inchworm assemblerはTrinitiyの中のアセンブラで知ってる人も多いと思う。TrinityのソースコードHPからダウンロードしてインストールする。 上記ファイルをzipでダウンロードして解凍。中にあるInchwormディレクトリに移動。
unzip trinityrnaseq-Trinity-v2.3.2.zip
cd trinityrnaseq-Trinity-v2.3.2/Inchworm/
マニュアルに従って Inchwormをビルド。
./configure --prefix=`pwd`
make
make install
bin/内に実行ファイル"inchworm"ができているはず。これにパスを通すかusr/bin内にコピー。
これでようやくランの準備が整った。
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Scanindelはconfioguration fileを読み込み、その内容に従って解析される。そのため依存ツールのリファレンスindexのパスを書いたconfig.txtと、サンプルのパスを書いたsample.txtを準備しておく必要がある。以下のようなファイルを用意した。
confg.txt
#name=path
bwa=/home/kazu/ScanIndel/genome/Human_chr19.fasta
blat=/home/kazu/ScanIndel/genome/
freebayes=/home/kazu/ScanIndel/genome/Human_chr19.fasta
sample.txt
user$ cat sample.txt
test TR1.fastq R2.fastq
blatのindexファイルは
faToTwoBit ref.fa ref.2bit
で作り、上の内容通りgenome/に置いておく。bwaのindexは
bwa index Human?chr19.fasta
で作成し、fastaと一緒にgenome/に配置しておく。Freebayesは同じfastaを指定するだけでO.K。
fastqのパスを指定する。今回は解析するカレントディレクトリにそのままfastqを置いたので、上のようになる。あとは以下のコマンドを打つとScanindelが実行される。
python ScanIndel.py -i sample.txt -p config.txt [options]
mappingが行われ、SV callまで自動で進む。
-------参考1----------------------------------------------------------------------
scanindelはリードとリファンレスの相同部位検索にblatを用いている。blatはblastに類似した相同部位検索プログラムで、indexファイルの作成がいらないなどの特徴をもつ。詳細はこちら
blatはスタンドアローンとwebサーバー版(UCSC)がある。最初にbinaryファイルを作るところは同じで、以下のコマンドを打つ(上の通り)。
faToTwoBit ref.fa ref.2bit
そのあとサーバー版ではgfServerコマンドを使いポートを開ける。
gfServer -trans -mask start localhost 17775 ref.2bit &
gfServer start localhost 17774 ref.2bit &
localhostは自分で指定する名前。
17774は自分で指定するポート番号。
----エラーが出たとき-----
ただしたくさんのスクリプトを統合しているためか、エラーが出てきたときはlogファイル(gfserver.temp.log)を開きどこで止まったか確認して進める。今回はbwa memのプロセスでエラーが出た。
これはsamtools sortコマンドがバージョンにより
samtools sort input.bam input_sorted
でsorted.bamができるbwaのバージョンと
samtools sort input.bam > input_sorted.bam
にしないとsortred.bamができないバージョンがあるかららしい。この件はgithubのScanindelのところでもコメントで表示されている。logにbwa memのソートでエラーが出ていた場合、pythonスクリプトを以下のように修正。
まずScanIndel.pyをテキストエディタで開く。
94行目の
"bwa.bam"+output+".bwa.sorted"
を
"bwa.bam >"+output+".bwa.sorted.bam"
に変更。さらに241行目の
'temp.bam' + output + '.temp.sorted'
を
'temp.bam >' + output + '.temp.sorted.bam'
に変更すれば動く。
-------参考2----------------------------------------------------------------------
ScanIndelは内部でblatを動かし、自動で上のコマンドを走らせポートを開けてリファレンスとのマッチを行う。そのため、blat検索時のポート番号の指定などのオプションを備えている。 ScanIndelのランに失敗すると、gfServerが停止せずポートが開きっぱなしになる。 このままだと、次回ランでエラーになる。ポート番号を--gfServer_portオプションで指定するか、ポートを閉じておく。ポートを閉じるには、まずポート番号をlsofコマンドで確認し、
lsof -i
表示されたプロセス番号が2587だとしたら
kill 2587
これで停止できる。その他、途中で止まるとログファイル(gfserver.temp.log)も残っている。これも次回ランでエラーを起こすぽいので、エラー内容を確認したら消しておく。 その他、シミュレーションででsmall indelを検出しようとすると、エラーログなしに解析が止まることもたくさんあった。その場合、large indelを少し加えると、ランは最後まで行くようになった。そのとき、small indelも正確に検出されていたので、何かしら小さなバグだと思われる。ランが途中で止まる人は、コントロールで大きなindelを加えてやり直してみてもいいかもしれない。
その他、シミューレーションデータで検証時、短いindelを検出しようとすると途中で止まることがあった。原因は不明だがlong indelを混ぜ込むとランは正常に終了したので、対処療法的にバグ回避はできたが原因は不明。
PRISM Jiang et al. (2012)
discordant paired read + split-read approaches.
linuxのみサポートされている。
インストールは
tar xvzf PRISM.x86_64.tar.gz
cd PRISM
file bin/smapper
export PRISM_PATH=$PWD
PRISMは大きく分けて4つのステップからなる。それらのtoolはtoolkitディレクトリ中に保存されている。ただし、実際のランはrun_PRISM.shを走らせるだけでよい。
テストランは
./run_PRISM.sh -m500 -e30 -i /home/user/PRISM_1_1_6/sample/chr100.sam -r /home/user/PRISM_1_1_6/sample/reference/chr100.fa
samファイルとfaファイルはフルパスで指定する。
ランが成功すると、カレントディレクトリにPRISM_outputができ、中にdiscordantなリードペアのクラスターがsam形式で出力される。これが構造変化の種類ごとに分けて出力されるのでかなりたくさんのsamができる(詳細はREADMEに書いてある)。肝心のindelはsplit_all.sam_ns_rmmul_cigar_sorted_svに保存されている。
パスを通してからのランは下のように行う。
run_PRISM.sh -m600 -e100 -i /home/user/input.sam -r /home/user/ref.fa -I PRISM_working_directory -O output
-Iと-Oでそれぞれ作業ディレクトリと出力ディレクトリを明示する。インサートサイズとSDを大きく間違うと途中で止まることがあるみたいので注意する。
Manta Chen et al. (2016)
discordant paired read + split-read approaches.
conda install -c bioconda- y manta
tumorとnormalを比較して、高い感受性でガン変異を検出する機能を持つ。
インストールガイドにはmacでも動作可能なはずと書かれているが、macはインストールが面倒だったので、binary版がダウンロードできるcent OSで進めた。
MantaはSun grid engineのような分散コンピュータ環境にも対応しているらしいが、ゲノムサイズがそれほど大きなければローカル環境で十分高速に動く。
はじめにbin/の中にあるconfigManta.pyにパスを通しておく。
ランは、はじめにコンフィグレーションファイルを作り、それを元に解析する2段階方式dである。
1、コンフィグディレクトリの作成。シングルのdiploidゲノムなら
configManta.py --bam NA12878_S1.bam --referenceFasta ref.fa --runDir oputput
--bam: ペアエンドのbamファイルの指定。
--referenceFasta: リファレンスfastaの指定。
--runDir: 出力ディレクトリ
2、ラン シングルdiploidデータ
python runWorkflow.py -m local -j 12
-m: --mode=MODE select run mode (local|sge)。ローカルなら"local"を指定。
-j: ジョブ数。SGE環境なら128まで対応。デフォルト8。
同じサンプルデータが複数あるときのコンフィグファイル作成 (fastqをマージしても同じ)
configManta.py --bam 1.bam --bam 2.bam --bam 3.bam --referenceFasta ref.fa --runDir oputput
Mantaはデフォルトではwhole genome DNA seq解析モードになっているが、オプションを指定することでRNA seq, exome、target seqの変異解析を行うことも可能になっている。
腫瘍と体細胞の比較時のコンフィグファイル作成
configManta.py --normalBam HCC1187BL.cram --tumorBam HCC1187C.cram --referenceFasta ref.fa --runDir oputput
腫瘍データのみの時のコンフィグファイル作成
configManta.py --tumorBam HCC1187C.cram --referenceFasta ref.fa --runDir oputput
RNA-seqデータ(まだ不完全らしい)
configManta.py --rna --Bam 1.bam --referenceFasta ref.fa --runDir oputput
RNAモードでは1データのみ現在は対応。
Topにリンクを追加しました。
感じたこと
シミュレーションデータでホモの構造変化の検出テストを行うと、Fermikit、ScanIndelが最も検出率が高く、コール内容も正確だった。次点でBreseq、pindelの検出率が高かった。特にPindelは特にレアな構造変化の検出に強かった。これはリードの個数を指定して感度をカバレッジに応じて変化できる点が効いていると思われる。
small indelの検出だと、Platypusとpindelの検出感度が優れていた。ただし2つとも、デフォルトではサポートするリードが2つでバリアントを検出する設定のため、ディープにシーケンスしたデータだとエラーも拾いやすい。1st screeningではオプションをつけて感度を下げて検出する工夫も必要と思われる。
補足
ツールによって異なる重み付けでSVはコールされており、どうやって統合するかについても論文で議論されています。1つペーパーのリンクを貼っておきます。
https://academic.oup.com/bib/article/16/5/852/217239/Making-the-difference-integrating-structural
追記
ゲノムをPolishできるPilonを使えば、bmaからSNV、small indel、large indelを検出しVCFで出力し、さらに変異を修正したfastaも自動出力してくれます。
追記
トップにもリンクを張りましたが、Parliament2は簡単に動かすことができるとても使いやすいツールです。オススメします。
追記
dbSTAR - a reference DataBase of human STructural vARiation from sequencing data
http://dbstar.lbgi.fr/dbstar/software
(開発中)
引用
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
BreakDancer
Identification of Genomic Structural Variation from Paired-End Read Mapping
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4138716/
LUMPY
A probabilistic framework for structural variant discovery
https://genomebiology.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/gb-2014-15-6-r84
Pindel
A pattern growth approach to detect break points of large deletions and medium sized insertions from paired-end short reads
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2781750/
GASVpro
An integrative probabilistic model for identification of structural variation in sequencing data
https://genomebiology.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/gb-2012-13-3-r22
DELLY2
Structural variant discovery by integrated paired-end and split-read analysis
PRISM
PRISM: Pair-read informed split-read mapping for base-pair level detection of insertion, deletion and structural variants
Platypus
Platypus: A New Variant Caller that Integrates Mapping, Assembly and Haplotype-based approaches
http://www.nature.com/ng/journal/v46/n8/full/ng.3036.html
FermiKit
FermiKit: assembly-based variant calling for Illumina resequencing data
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4757955/
Freebayes
Haplotype-based variant detection from short-read sequencing
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1207.3907.pdf
SvABA
SvABA: Genome-wide detection of structural variants and indels by local assembly
http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/02/01/105080.full.pdf
VarScan
VarScan: variant detection in massively parallel sequencing of individual and pooled samples
Scalpel
Accurate de novo and transmitted indel detection in exome-capture data using microassembly
http://www.nature.com/nmeth/journal/v11/n10/full/nmeth.3069.html
Breakseek
BreakSeek: a breakpoint-based algorithm for full spectral range INDEL detection
INDELseek
INDELseek: detection of complex insertions and deletions from next-generation sequencing data
https://bmcgenomics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12864-016-3449-9
Breseq
Identifying structural variation in haploid microbial genomes from short-read resequencing data using breseq
https://bmcgenomics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1471-2164-15-1039
ScanIndel
ScanIndel: a hybrid framework for indel detection via gapped alignment, split reads and de novo assembly
https://genomemedicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13073-015-0251-2
PRISM
PRISM: Pair-read informed split-read mapping for base-pair level detection of insertion, deletion and structural variants
https://genomemedicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13073-015-0251-2
Manta
Manta: rapid detection of structural variants and indels for germline and cancer sequencing applications
https://academic.oup.com/bioinformatics/article-lookup/doi/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv710
MetaSV
An accurate and integrative structural-variant caller for next generation sequencing
Bioinformatics first published online April 10, 2015 doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btv204
2022/07/06
STAR ProtocolジャーナルにSV callingのビギナーズガイド論文が出版されています( Open access)。実際の解析の流れを学ことができます。