2020 7/21 出力画像追加
構造変異とは、50 bpよりも大きいゲノム変異と定義されている。構造変異は、一塩基多型や小さな挿入・欠失よりも、任意のゲノムのより多くの塩基に影響を与えることが示されている。さらに、これらの変異はヒトの表現型や多様性に大きな影響を与え、多くの疾患と関連している。それらのサイズとリピートとの関連性のため、ショットガンシーケンシングでは、特にショートリードに基づいている場合には検出が困難である。Pacific BiosciencesやOxford Nanopore Technologiesが提供するようなロングリード、1分子シーケンシング技術は、数千塩基対の長さのリードを生成する。より高いエラー率とシークエンシングコストにもかかわらず、ロングリードシークエンシングは構造変異の検出に多くの利点をもたらす。しかし、利用可能なソフトウェアツールでは、その可能性を十分に活用できていないのが現状である。
本研究では、ロングリードデータから構造バリアントを高感度に検出し、正確に特徴付けするためのツールであるSVIMを紹介する。SVIMは、リードアラインメントからの構造バリアントシグネチャの収集、クラスタリング、および組み合わせのための3つのコンポーネントから構成されている。SVIMは、タンデム重複やインタースパン重複、新規エレメント挿入などの類似したタイプを含む5つの異なるバリアントクラスを識別する。SVIMは、ゲノム上の重複の発生源と発生先の両方を抽出できる点でユニークである。Pacific Biosciences社とNanopore社のシーケンシングマシンによるシミュレーションデータと実データでの評価では、既存のツールと比較して良好な結果が得られている。
SVIM のソースコードと実行ファイルは Github: github.com/eldariont/svim で公開されている。SVIMはPython 3で実装されており、biocondaとPythonパッケージインデックスで利用できる。
SVIMは4つの主要なステップで構成される。
COLLECTは、ロングリードアラインメントのSVのシグネチャを検出する。
CLUSTER は同じ SV からのシグネチャをマージする。
COMBINEは、異なるゲノム領域からのクラスタを結合し、異なるSVタイプに分類する。
GENOTYPEはSVにまたがるアラインメントを用いて遺伝子型を決定する。
https://github.com/eldariont/svim/wiki
raw long readsではなくハプロイドや二倍体ゲノムアセンブリ、またはコンティグを解析する場合は、別の方法であるSVIM-asmを使う。
インストール
ubuntu18.04LTSでテストした。
#bioconda (link)
conda create -n svim_env --channel bioconda svim
conda activate svim_env
#pip (Python 3.6 or newer)
pip install svim
#Install from github
git clone https://github.com/eldariont/svim.git
cd svim
pip install .
> svim -h
$ svim -h
usage: svim [-h] [--version] {reads,alignment} ...
SVIM (pronounced SWIM) is a structural variant caller for long reads.
It discriminates five different variant classes: deletions, tandem and interspersed duplications,
inversions and insertions. SVIM is unique in its capability of extracting both the genomic origin and
destination of duplications.
SVIM consists of four major steps:
- COLLECT detects signatures for SVs in long read alignments
- CLUSTER merges signatures that come from the same SV
- COMBINE combines clusters from different genomic regions and classifies them into distinct SV types
- GENOTYPE uses alignments spanning SVs to determine their genotype
SVIM can process two types of input. Firstly, it can detect SVs from raw reads by aligning them to a given reference genome first ("SVIM.py reads [options] working_dir reads genome").
Alternatively, it can detect SVs from existing reads alignments in SAM/BAM format ("SVIM.py alignment [options] working_dir bam_file").
positional arguments:
{reads,alignment} modes
reads Detect SVs from raw reads. Align reads to given reference
genome first.
alignment Detect SVs from an existing alignment
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--version, -v show program's version number and exit
> svim reads -h
$ svim reads -h
usage: svim reads [-h] [--verbose] [--cores CORES]
[--aligner {ngmlr,minimap2}] [--nanopore]
[--min_mapq MIN_MAPQ] [--min_sv_size MIN_SV_SIZE]
[--max_sv_size MAX_SV_SIZE]
[--segment_gap_tolerance SEGMENT_GAP_TOLERANCE]
[--segment_overlap_tolerance SEGMENT_OVERLAP_TOLERANCE]
[--all_bnds]
[--partition_max_distance PARTITION_MAX_DISTANCE]
[--distance_normalizer DISTANCE_NORMALIZER]
[--cluster_max_distance CLUSTER_MAX_DISTANCE]
[--del_ins_dup_max_distance DEL_INS_DUP_MAX_DISTANCE]
[--trans_destination_partition_max_distance TRANS_DESTINATION_PARTITION_MAX_DISTANCE]
[--trans_partition_max_distance TRANS_PARTITION_MAX_DISTANCE]
[--trans_sv_max_distance TRANS_SV_MAX_DISTANCE]
[--skip_genotyping] [--minimum_score MINIMUM_SCORE]
[--homozygous_threshold HOMOZYGOUS_THRESHOLD]
[--heterozygous_threshold HETEROZYGOUS_THRESHOLD]
[--minimum_depth MINIMUM_DEPTH] [--sample SAMPLE]
[--types TYPES] [--sequence_alleles] [--insertion_sequences]
[--tandem_duplications_as_insertions]
[--interspersed_duplications_as_insertions] [--read_names]
[--zmws]
working_dir reads genome
positional arguments:
working_dir Working and output directory. Existing files in the
directory are overwritten. If the directory does not
exist, it is created.
reads Read file (FASTA, FASTQ, gzipped FASTA, gzipped FASTQ
or file list). The read file has to have one of the
following supported file endings: FASTA: .fa, .fasta,
.FA, .fa.gz, .fa.gzip, .fasta.gz, .fasta.gzip FASTQ:
.fq, .fastq, .FQ, .fq.gz, .fq.gzip, .fastq.gz,
.fastq.gzip FILE LIST: .fa.fn, fq.fn
genome Reference genome file (FASTA)
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--verbose Enable more verbose logging (default: False)
ALIGN:
--cores CORES CPU cores to use for the alignment (default: 1)
--aligner {ngmlr,minimap2}
Tool for read alignment: ngmlr or minimap2 (default:
ngmlr)
--nanopore Use Nanopore settings for read alignment (default:
False)
COLLECT:
--min_mapq MIN_MAPQ Minimum mapping quality of reads to consider (default:
20). Reads with a lower mapping quality are ignored.
--min_sv_size MIN_SV_SIZE
Minimum SV size to detect (default: 40). SVIM can
potentially detect events of any size but is limited
by the signal-to-noise ratio in the input alignments.
That means that more accurate reads and alignments
enable the detection of smaller events. For current
PacBio or Nanopore data, we would recommend a minimum
size of 40bp or larger.
--max_sv_size MAX_SV_SIZE
Maximum SV size to detect (default: 100000). This
parameter is used to distinguish long deletions (and
inversions) from translocations which cannot be
distinguished from the alignment alone. Split read
segments mapping far apart on the reference could
either indicate a very long deletion (inversion) or a
translocation breakpoint. SVIM calls a translocation
breakpoint if the mapping distance is larger than this
parameter and a deletion (or inversion) if it is
smaller or equal.
--segment_gap_tolerance SEGMENT_GAP_TOLERANCE
Maximum tolerated gap between adjacent alignment
segments (default: 10). This parameter applies to gaps
on the reference and the read. Example: Deletions are
detected from two subsequent segments of a split read
that are mapped far apart from each other on the
reference. The segment gap tolerance determines the
maximum tolerated length of the read gap between both
segments. If there is an unaligned read segment larger
than this value between the two segments, no deletion
is called.
--segment_overlap_tolerance SEGMENT_OVERLAP_TOLERANCE
Maximum tolerated overlap between adjacent alignment
segments (default: 5). This parameter applies to
overlaps on the reference and the read. Example:
Deletions are detected from two subsequent segments of
a split read that are mapped far apart from each other
on the reference. The segment overlap tolerance
determines the maximum tolerated length of an overlap
between both segments on the read. If the overlap
between the two segments on the read is larger than
this value, no deletion is called.
--all_bnds Output all rearrangements additionally in BND notation
(default: False). By default, SV signatures from the
read alignments are used to detect complete SVs, such
as deletions, insertions and inversions. When this
option is enabled, all SVs are also output in breakend
(BND) notation as defined in the VCF specs. For
instance, a deletion gets two records in the VCF
output: 1. the normal <DEL> record and 2. a <BND>
record representing the novel adjacency between the
deletion's start and end coordinate in the sample
genome.
CLUSTER:
--partition_max_distance PARTITION_MAX_DISTANCE
Maximum distance in bp between SVs in a partition
(default: 1000). Before clustering, the SV signatures
are divided into coarse partitions. This parameter
determines the maximum distance between two subsequent
signatures in the same partition. If the distance
between two subsequent signatures is larger than this
parameter, they are distributed into separate
partitions.
--distance_normalizer DISTANCE_NORMALIZER
Distance normalizer used for span-position distance
(default: 900). SVIM clusters the SV signatures using
an hierarchical clustering approach and a novel
distance metric called "span-position distance". Span-
position distance is the sum of two components, span
distance and position distance. The span distance is
the difference in lengths between signatures
normalized by the greater length and always lies in
the interval [0,1]. The position distance is the
difference in position between signatures normalized
by the distance normalizer (this parameter). For a
position difference of 1.8kb and a distance normalizer
of 900, the position distance will be 2. A smaller
distance normalizer leads to a higher position
distance and as a consequence increases the importance
of the position distance in the span-position distance
relative to the span distance.
--cluster_max_distance CLUSTER_MAX_DISTANCE
Maximum span-position distance between SVs in a
cluster (default: 0.3). This is the most important
parameter because it determines the strictness of
clustering. Choosing a large value leads to fewer but
larger clusters with larger distances between its
members. Choosing a small value leads to more but
smaller clusters with smaller distances between its
members. This parameter determines the height of the
cut-off in the hierarchical clustering dendrogram.
COMBINE:
--del_ins_dup_max_distance DEL_INS_DUP_MAX_DISTANCE
Maximum span-position distance between the origin of
an insertion and a deletion to be flagged as a
potential cut&paste insertion (default: 1.0)
--trans_destination_partition_max_distance TRANS_DESTINATION_PARTITION_MAX_DISTANCE
Maximum distance in bp between translocation
breakpoint destinations in a partition (default: 1000)
--trans_partition_max_distance TRANS_PARTITION_MAX_DISTANCE
Maximum distance in bp between translocation
breakpoints in a partition (default: 200)
--trans_sv_max_distance TRANS_SV_MAX_DISTANCE
Maximum distance in bp between a translocation
breakpoint and an SV signature to be combined
(default: 500)
GENOTYPE:
--skip_genotyping Disable genotyping (default: False)
--minimum_score MINIMUM_SCORE
Minimum score for genotyping (default: 3). Only SV
candidates with a higher or equal score are genotyped.
Depending on the score distribution among the SV
candidates, decreasing this value increases the
runtime. We recommend to choose a value close to the
score threshold used for filtering the SV candidates.
--homozygous_threshold HOMOZYGOUS_THRESHOLD
Minimum variant allele frequency to be called as
homozygous (default: 0.8). Allele frequency is
computed as the fraction of reads supporting the
variant over the total number of reads covering the
variant. Variants with an allele frequence greater
than or equal to this threshold are called as
homozygous alternative.
--heterozygous_threshold HETEROZYGOUS_THRESHOLD
Minimum variant allele frequency to be called as
heterozygous (default: 0.2). Allele frequency is
computed as the fraction of reads supporting the
variant over the total number of reads covering the
variant. Variants with an allele frequence greater
than or equal to this threshold but lower than the
homozygous threshold are called as heterozygous
alternative. Variants with an allele frequence lower
than this threshold are called as homozygous
reference.
--minimum_depth MINIMUM_DEPTH
Minimum total read depth for genotyping (default: 4).
Variants covered by a total number of reads lower than
this value are not assigned a genotype (./. in the
output VCF file).
OUTPUT:
--sample SAMPLE Sample ID to include in output vcf file (default:
Sample)
--types TYPES SV types to include in output VCF (default:
DEL,INS,INV,DUP:TANDEM,DUP:INT,BND). Give a comma-
separated list of SV types. The possible SV types are:
DEL (deletions), INS (novel insertions), INV
(inversions), DUP:TANDEM (tandem duplications),
DUP:INT (interspersed duplications), BND (breakends).
--sequence_alleles Use nucleotide sequences for alleles of deletions,
inversions and insertions in output VCF (default:
False). By default, all SVs are represented by
symbolic alleles, such as <DEL>, <INV> or <INS>. If
enabled, ALT alleles of insertions are obtained from
the sequence of a random read that supports the
variant.
--insertion_sequences
Output insertion sequences in INFO tag of VCF
(default: False). If enabled, the INFO/SEQS tag
contains a list of insertion sequences from the
supporting reads. However, the insertion sequences are
not combined into a consensus sequence.
--tandem_duplications_as_insertions
Represent tandem duplications as insertions in output
VCF (default: False). By default, tandem duplications
are represented by the SVTYPE=DUP:TANDEM and the
genomic source is given by the POS and END tags. When
enabling this option, duplications are instead
represented by the SVTYPE=INS and POS and END both
give the insertion point of the duplication.
--interspersed_duplications_as_insertions
Represent interspersed duplications as insertions in
output VCF (default: False). By default, interspersed
duplications are represented by the SVTYPE=DUP:INT and
the genomic source is given by the POS and END tags.
When enabling this option, duplications are instead
represented by the SVTYPE=INS and POS and END both
give the insertion point of the duplication.
--read_names Output names of supporting reads in INFO tag of VCF
(default: False). If enabled, the INFO/READS tag
contains the list of names of the supporting reads.
--zmws look for information on ZMWs in PacBio read names
(default: False). If enabled, the INFO/ZMWS tag
contains the number of ZMWs that produced supporting
reads.
> svim alignment -h
$ svim alignment -h
usage: svim alignment [-h] [--verbose] [--min_mapq MIN_MAPQ]
[--min_sv_size MIN_SV_SIZE] [--max_sv_size MAX_SV_SIZE]
[--segment_gap_tolerance SEGMENT_GAP_TOLERANCE]
[--segment_overlap_tolerance SEGMENT_OVERLAP_TOLERANCE]
[--partition_max_distance PARTITION_MAX_DISTANCE]
[--distance_normalizer DISTANCE_NORMALIZER]
[--cluster_max_distance CLUSTER_MAX_DISTANCE]
[--all_bnds]
[--del_ins_dup_max_distance DEL_INS_DUP_MAX_DISTANCE]
[--trans_destination_partition_max_distance TRANS_DESTINATION_PARTITION_MAX_DISTANCE]
[--trans_partition_max_distance TRANS_PARTITION_MAX_DISTANCE]
[--trans_sv_max_distance TRANS_SV_MAX_DISTANCE]
[--skip_genotyping] [--minimum_score MINIMUM_SCORE]
[--homozygous_threshold HOMOZYGOUS_THRESHOLD]
[--heterozygous_threshold HETEROZYGOUS_THRESHOLD]
[--minimum_depth MINIMUM_DEPTH] [--sample SAMPLE]
[--types TYPES] [--sequence_alleles]
[--insertion_sequences]
[--tandem_duplications_as_insertions]
[--interspersed_duplications_as_insertions]
[--read_names] [--zmws]
working_dir bam_file genome
positional arguments:
working_dir Working and output directory. Existing files in the
directory are overwritten. If the directory does not
exist, it is created.
bam_file Coordinate-sorted and indexed BAM file with aligned
long reads
genome Reference genome file that the long reads were aligned
to (FASTA)
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--verbose Enable more verbose logging (default: False)
COLLECT:
--min_mapq MIN_MAPQ Minimum mapping quality of reads to consider (default:
20). Reads with a lower mapping quality are ignored.
--min_sv_size MIN_SV_SIZE
Minimum SV size to detect (default: 40). SVIM can
potentially detect events of any size but is limited
by the signal-to-noise ratio in the input alignments.
That means that more accurate reads and alignments
enable the detection of smaller events. For current
PacBio or Nanopore data, we would recommend a minimum
size of 40bp or larger.
--max_sv_size MAX_SV_SIZE
Maximum SV size to detect (default: 100000). This
parameter is used to distinguish long deletions (and
inversions) from translocations which cannot be
distinguished from the alignment alone. Split read
segments mapping far apart on the reference could
either indicate a very long deletion (inversion) or a
translocation breakpoint. SVIM calls a translocation
breakpoint if the mapping distance is larger than this
parameter and a deletion (or inversion) if it is
smaller or equal.
--segment_gap_tolerance SEGMENT_GAP_TOLERANCE
Maximum tolerated gap between adjacent alignment
segments (default: 10). This parameter applies to gaps
on the reference and the read. Example: Deletions are
detected from two subsequent segments of a split read
that are mapped far apart from each other on the
reference. The segment gap tolerance determines the
maximum tolerated length of the read gap between both
segments. If there is an unaligned read segment larger
than this value between the two segments, no deletion
is called.
--segment_overlap_tolerance SEGMENT_OVERLAP_TOLERANCE
Maximum tolerated overlap between adjacent alignment
segments (default: 5). This parameter applies to
overlaps on the reference and the read. Example:
Deletions are detected from two subsequent segments of
a split read that are mapped far apart from each other
on the reference. The segment overlap tolerance
determines the maximum tolerated length of an overlap
between both segments on the read. If the overlap
between the two segments on the read is larger than
this value, no deletion is called.
CLUSTER:
--partition_max_distance PARTITION_MAX_DISTANCE
Maximum distance in bp between SVs in a partition
(default: 1000). Before clustering, the SV signatures
are divided into coarse partitions. This parameter
determines the maximum distance between two subsequent
signatures in the same partition. If the distance
between two subsequent signatures is larger than this
parameter, they are distributed into separate
partitions.
--distance_normalizer DISTANCE_NORMALIZER
Distance normalizer used for span-position distance
(default: 900). SVIM clusters the SV signatures using
an hierarchical clustering approach and a novel
distance metric called "span-position distance". Span-
position distance is the sum of two components, span
distance and position distance. The span distance is
the difference in lengths between signatures
normalized by the greater length and always lies in
the interval [0,1]. The position distance is the
difference in position between signatures normalized
by the distance normalizer (this parameter). For a
position difference of 1.8kb and a distance normalizer
of 900, the position distance will be 2. A smaller
distance normalizer leads to a higher position
distance and as a consequence increases the importance
of the position distance in the span-position distance
relative to the span distance.
--cluster_max_distance CLUSTER_MAX_DISTANCE
Maximum span-position distance between SVs in a
cluster (default: 0.3). This is the most important
parameter because it determines the strictness of
clustering. Choosing a large value leads to fewer but
larger clusters with larger distances between its
members. Choosing a small value leads to more but
smaller clusters with smaller distances between its
members. This parameter determines the height of the
cut-off in the hierarchical clustering dendrogram.
--all_bnds Output all rearrangements additionally in BND notation
(default: False). By default, SV signatures from the
read alignments are used to detect complete SVs, such
as deletions, insertions and inversions. When this
option is enabled, all SVs are also output in breakend
(BND) notation as defined in the VCF specs. For
instance, a deletion gets two records in the VCF
output: 1. the normal <DEL> record and 2. a <BND>
record representing the novel adjacency between the
deletion's start and end coordinate in the sample
genome.
COMBINE:
--del_ins_dup_max_distance DEL_INS_DUP_MAX_DISTANCE
Maximum span-position distance between the origin of
an insertion and a deletion to be flagged as a
potential cut&paste insertion (default: 1.0)
--trans_destination_partition_max_distance TRANS_DESTINATION_PARTITION_MAX_DISTANCE
Maximum distance in bp between translocation
breakpoint destinations in a partition (default: 1000)
--trans_partition_max_distance TRANS_PARTITION_MAX_DISTANCE
Maximum distance in bp between translocation
breakpoints in a partition (default: 200)
--trans_sv_max_distance TRANS_SV_MAX_DISTANCE
Maximum distance in bp between a translocation
breakpoint and an SV signature to be combined
(default: 500)
GENOTYPE:
--skip_genotyping Disable genotyping (default: False)
--minimum_score MINIMUM_SCORE
Minimum score for genotyping (default: 3). Only SV
candidates with a higher or equal score are genotyped.
Depending on the score distribution among the SV
candidates, decreasing this value increases the
runtime. We recommend to choose a value close to the
score threshold used for filtering the SV candidates.
--homozygous_threshold HOMOZYGOUS_THRESHOLD
Minimum variant allele frequency to be called as
homozygous (default: 0.8). Allele frequency is
computed as the fraction of reads supporting the
variant over the total number of reads covering the
variant. Variants with an allele frequence greater
than or equal to this threshold are called as
homozygous alternative.
--heterozygous_threshold HETEROZYGOUS_THRESHOLD
Minimum variant allele frequency to be called as
heterozygous (default: 0.2). Allele frequency is
computed as the fraction of reads supporting the
variant over the total number of reads covering the
variant. Variants with an allele frequence greater
than or equal to this threshold but lower than the
homozygous threshold are called as heterozygous
alternative. Variants with an allele frequence lower
than this threshold are called as homozygous
reference.
--minimum_depth MINIMUM_DEPTH
Minimum total read depth for genotyping (default: 4).
Variants covered by a total number of reads lower than
this value are not assigned a genotype (./. in the
output VCF file).
OUTPUT:
--sample SAMPLE Sample ID to include in output vcf file (default:
Sample)
--types TYPES SV types to include in output VCF (default:
DEL,INS,INV,DUP:TANDEM,DUP:INT,BND). Give a comma-
separated list of SV types. The possible SV types are:
DEL (deletions), INS (novel insertions), INV
(inversions), DUP:TANDEM (tandem duplications),
DUP:INT (interspersed duplications), BND (breakends).
--sequence_alleles Use nucleotide sequences for alleles of deletions,
inversions and insertions in output VCF (default:
False). By default, all SVs are represented by
symbolic alleles, such as <DEL>, <INV> or <INS>. If
enabled, ALT alleles of insertions are obtained from
the sequence of a random read that supports the
variant.
--insertion_sequences
Output insertion sequences in INFO tag of VCF
(default: False). If enabled, the INFO/SEQS tag
contains a list of insertion sequences from the
supporting reads. However, the insertion sequences are
not combined into a consensus sequence.
--tandem_duplications_as_insertions
Represent tandem duplications as insertions in output
VCF (default: False). By default, tandem duplications
are represented by the SVTYPE=DUP:TANDEM and the
genomic source is given by the POS and END tags. When
enabling this option, duplications are instead
represented by the SVTYPE=INS and POS and END both
give the insertion point of the duplication.
--interspersed_duplications_as_insertions
Represent interspersed duplications as insertions in
output VCF (default: False). By default, interspersed
duplications are represented by the SVTYPE=DUP:INT and
the genomic source is given by the POS and END tags.
When enabling this option, duplications are instead
represented by the SVTYPE=INS and POS and END both
give the insertion point of the duplication.
--read_names Output names of supporting reads in INFO tag of VCF
(default: False). If enabled, the INFO/READS tag
contains the list of names of the supporting reads.
--zmws look for information on ZMWs in PacBio read names
(default: False). If enabled, the INFO/ZMWS tag
contains the number of ZMWs that produced supporting
reads.
実行方法
生のロングリードを与えられたリファレンスゲノムにアラインメントすることで、生のロングリードからSVを検出することができる。また、SAM/BAMフォーマットの既存のリードアライメントからSVを検出することもできる。
デフォルトのngmlrを使ってリードをアラインし、SVをコール。
#PacBio reads
svim reads out_dir input_reads.fa ref.fa
#ONT reads
svim reads --nanopore out_dir input_reads.fa ref.fa
指定したout_dirディレクトリにログファイル、VCF 形式の SVコール結果、BED 形式の SVコール結果、BED形式の中間シグネチャクラスタが出力される。
minimap2を使ってリードをアラインし、SVをコール。
#PacBio reads
svim reads --aligner minimap2 out_dir input_reads.fa ref.fa
#Use only high-quality alignments
svim reads --min_mapq 30 out_dir input_reads.fa ref.fa
bamを指定する。
svim alignment my_sample input.bam
出力
variants.vcf
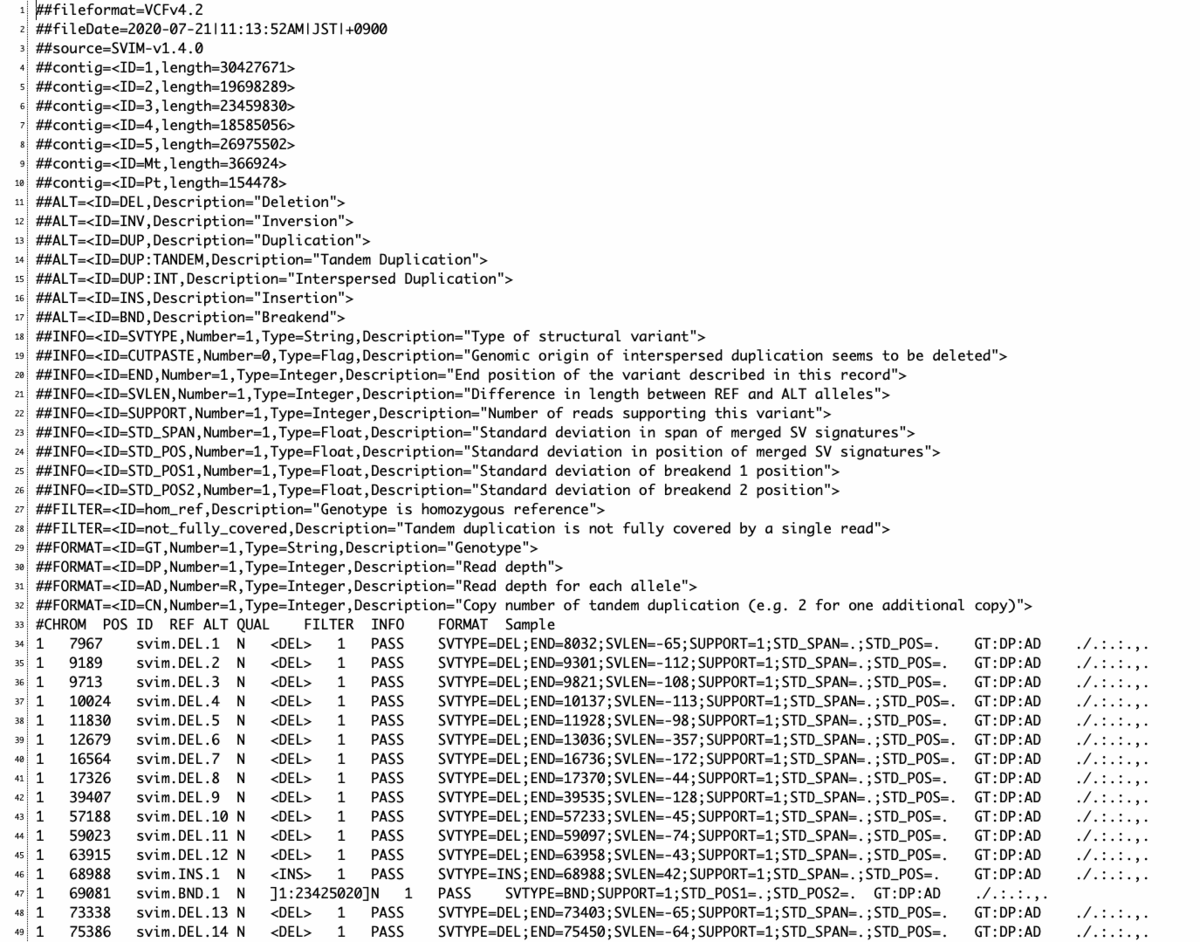
- SVIM は全ての SVコールとスコアを出力する。そのため、結果をこれらのスコアに基づいてフィルタリングすることが強く推奨されている。これはすべてのバリアントコールを出力して、フィルタリングを後処理のステップとして残した方が、よりユーザーフレンドリーであるというオーサーらの考えによる。
- SVIM は各 variant コールに対して 0 から 100 の間のスコアを出力する。スコアが高いほど、そのコールがより信頼できることを意味する。スコアはVCF出力のQUAL列やBEDファイルの5番目の列にある。スコアは主にサポートするリードの数に基づいており。さらにSVのスパンと位置に関するサポートリード間の一致も考慮されている。
- 結果のフィルタリングに関してだが、スコアがサポートリード数に依存するため、そのスコア分布は入力のシーケンシングカバレッジに応じて変化する。したがって、適切なスコアカットオフについて一概には言えない。カバレッジの高いデータセット(>40倍)では、10-15のしきい値が推奨される。カバー率の低いデータセットでは,閾値を低くすべきである。
引用
SVIM: structural variant identification using mapped long reads
David Heller, Martin Vingron
Bioinformatics, Volume 35, Issue 17, 1 September 2019