配列決定されたゲノムの数が増え続けており、比較ゲノムのためのパンゲノムアプローチの開発が必要とされている。2016年に発表されたPanToolsは、パンゲノム構築、ホモロジーグループ化、パンゲノムリードマッピングを可能にするプラットフォームである。グラフデータベース技術を使用しているため、SARS-CoV-2のような小さなウイルスゲノムから、トマトやヒトのような大きな植物や動物のゲノムまで、PanToolsは多用途に適用できる。ここでは、機能アノテーションの統合を可能にし、遺伝子レベルの解析と系統樹の両方を提供するPanToolsの3回目のメジャーアップデートを紹介する。
PanToolsはJava 8で実装され、GNU GPLv3ライセンスで公開されている。ソフトウェアとドキュメントは、https://git.wur.nl/bioinformatics/pantools で入手できる。
Documentation
https://pantools.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
インストール
ubuntu18に以下の手順で導入した。macでも導入可能と書かれている(Document参照)。
#conda (link)
conda config --set auto_activate_base false
conda config --add channels bioconda
conda config --add channels conda-forge
conda config --remove channels defaults
conda config --set channel_priority strict
mamba create -n pantools pantools bcftools busco
conda activate pantools
> pantools
Usage: pantools <databaseDirectory> COMMAND
<databaseDirectory> Path to the database root directory.
Commands:
characterization of gene and k-mer content
core_unique_thresholds Test the effect of changing the core
and unique threshold.
k_mer_classification, kmer_classification
Calculate the number of core,
accessory, unique, (and phenotype
specific) k-mer sequences.
pangenome_structure Determine the openness of the
pangenome based on homology groups
or k-mer sequences.
gene_classification Classify the gene repertoire as core,
accessory or unique.
grouping_overview Create an overview table for every
homology grouping in the pangenome.
characterization of functional annotations
function_overview Create an overview table for each
functional annotation type in the
pangenome.
functional_classification Classify functional annotations as
core, accessory or unique.
go_enrichment Identify over- or underrepresented GO
terms in a set of genes.
phylogenetic methods
ani Calculate Average Nucleotide Identity
(ANI) scores between genomes.
mlsa_concatenate Step 2/3 of mlsa. Concatenate the gene
selection into a single continuous
sequence.
consensus_tree Create a consensus tree by combining
gene trees from homology groups
using ASTRAL-Pro. By default, only
nucleotide sequences are aligned for
pangenome databases and only protein
sequences are aligned for
panproteome databases. If variants
are present in the pangenome, these
will be used as well.
mlsa Step 3/3 of mlsa. Run IQ-tree on the
concatenated sequences.
mlsa_find_genes Step 1/3 of mlsa. Search and filter
suitable genes for the mlsa.
core_phylogeny, core_snp_tree Create a SNP tree from single-copy
genes. By default, only nucleotide
sequences are aligned for pangenome
databases and only protein sequences
are aligned for panproteome
databases. If variants are present
in the pangenome, these will be used
as well.
remove data from the pangenome or panproteome
remove_pavs, remove_pav Remove PAV data from the pangenome.
remove_variants, remove_variant Remove variant data from the pangenome.
move_grouping Deactivate the currently active
homology grouping.
remove_annotations Remove all the genomic features that
belong to annotations.
remove_nodes Remove a selection of nodes and their
relationships from the pangenome.
remove_phenotypes Delete phenotype nodes or remove
specific phenotype information from
the nodes.
remove_functions Remove functional annotations from the
pangenome.
remove_grouping Remove an homology grouping from the
pangenome.
add annotation features to the genome
add_annotations Construct or expand the annotations of
an existing pangenome.
add_phenotypes Add phenotype data to the pangenome.
add_antismash Add antiSMASH gene clusters to the
pangenome.
add_variants, add_variant Add variant data to the pangenome.
add_pavs, add_pav Add PAV data to the pangenome.
busco_protein Identify BUSCO genes in the pangenome.
add_functions Add functional annotations to the
pangenome.
read mapping
map Map single or paired-end short reads
to one or multiple genomes in the
pangenome. One SAM or BAM file is
generated for each genome included
in the analysis.
phylogenetic tree editing
create_tree_template Create templates for coloring
phylogenetic trees in iTOL.
rename_phylogeny Update or alter the terminal nodes
(leaves) of a phylogenic tree.
root_phylogeny (Re)root a phylogenetic tree.
build a pangenome
add_genomes Add additional genomes to an existing
pangenome.
build_pangenome Build a pangenome from a set of
genomes. Please see the manual with
'build_pangenome --manual' for a
description of the options.
detect homology groups
group Generate homology groups based on
similarity of protein sequences.
change_grouping Change the active version of the
homology grouping.
optimal_grouping Find the most suitable settings for
group.
retrieve regions or features
retrieve_features Retrieve the sequence of annotated
features from the pangenome.
retrieve_regions Retrieve the sequence of genomic
regions from the pangenome.
find genes
find_genes_in_region Find genes in a given genomic region.
find_genes_by_name Find your genes of interest in the
pangenome by using the gene name and
extract the nucleotide and protein
sequence.
find_genes_by_annotation Find genes of interest in the
pangenome that share a functional
annotation node and extract the
nucleotide and protein sequence.
functional annotation info
show_go For a given GO term, show the child
terms, all parent terms higher in
the hierarchy, and connected mRNA
nodes.
compare_go For two given GO terms, move up in the
GO hierarchy to see if they are
related.
characterization of a pangenome
metrics Generates relevant metrics of the
pangenome and the individual genomes
and sequences.
variation_overview Write an overview of all accessions
added to the pangenome (both VCF and
PAV information).
build a panproteome
build_panproteome Build a panproteome from a set of
proteins.
matrix files
rename_matrix Rename the headers (first row and
leftmost column) of CSV formatted
matrix files.
order_matrix Order the values of a matrix file
created by PanTools.
sequence alignments
msa Create multiple sequence alignments.
By default, only nucleotide
sequences are aligned for pangenome
databases and only protein sequences
are aligned for panproteome
databases. If variants were added to
a pangenome, these will be aligned
by default. Required software:
MAFFT, FastTree.
export pangenome
export_pangenome Export a pangenome built with
build_pangenome into node
properties, relationship properties
and node sequence anchors files.
gene locations
locate_genes Identify and compare gene clusters of
from a set of homology groups.
homology group info
group_info Report all available information of
one or multiple homology groups.
The full manual and tutorial can be accessed using pantools --manual, or go to
the latest stable version at https://pantools.readthedocs.io/en/stable/.
For more information on the required and optional parameters per command, call
pantools COMMAND --help; or call pantools COMMAND --manual to open the detailed
command explanation in browser.
> pantools build_pangenome -h
Usage: pantools build_pangenome [--keep-intermediate-files]
[--cache-size=<cacheSize>]
[--kmer-size=<kSize>]
[--num-buckets=<numBuckets>]
[--num-db-writer-threads=<numDbWriterThreads>]
[--scratch-directory=<scratchDirectory>]
[-t=<nThreads>]
[--transaction-size=<transactionSize>]
<databaseDirectory> <genomesFile>
Build a pangenome from a set of genomes. Please see the manual with
'build_pangenome --manual' for a description of the options.
Required software: KMC 2.3 or 3.0.
<databaseDirectory> Path to the database root directory.
<genomesFile> A text file containing paths to FASTA files of
genomes; each in a separate line.
-t, --threads=<nThreads> Number of parallel working threads, default is the
number of cores or 8, whichever is lower.
--kmer-size=<kSize> Size of k-mers. Should be in range [6..255]. By
not giving this argument, the most optimal k-mer
size is calculated automatically.
--scratch-directory=<scratchDirectory>
Temporary directory for storing localization
update files.
--num-buckets=<numBuckets>
Number of buckets for sorting (default: 200).
--transaction-size=<transactionSize>
Number of localization updates to pack into a
single Neo4j transaction (default: 10000).
--num-db-writer-threads=<numDbWriterThreads>
Number of threads to use for writing to Neo4j
(default: 2).
--cache-size=<cacheSize>
Maximum number of items in the node properties
cache (default: 10000000).
--keep-intermediate-files
Do not delete intermediate localization files
after the command finishes.
> pantools build_panproteome -h
Usage: pantools build_panproteome <databaseDirectory> <proteomesFile>
Build a panproteome from a set of proteins.
Required software: KMC 2.3 or 3.0.
<databaseDirectory> Path to the database root directory.
<proteomesFile> A text file containing paths to FASTA files of
proteins to be added to the panproteome; each on
a separate line.
> pantools group -h
pantools group -h
Usage: pantools group [OPTIONS] <databaseDirectory>
Generate homology groups based on similarity of protein sequences.
Required software: MCL
<databaseDirectory> Path to the database root directory.
-t, --threads=<nThreads> Number of parallel working threads, default is the
number of cores or 8, whichever is lower.
-e, --exclude=<exclude> Exclude a selection of genomes.
-i, --include=<include> Only include a selection of genomes.
-A, --annotations-file=<annotationsFile>
A text file with the identifiers of annotations to
be included.
--longest Only cluster protein sequences of the longest
transcript per gene.
--scoring-matrix=<scoringMatrix>
The scoring matrix used (default: BLOSUM62).
--relaxation=<params> The relaxation in homology calls. Should be in
range [1..8], from strict to relaxed. Use
optimal_grouping to determine the best
relaxation setting.
--similarity-threshold=<similarityThreshold>
The minimum normalized similarity score of two
proteins. Should be in range [1..99].
--contrast=<contrast> The contrast factor. Should be in range [0,10].
--intersection-rate=<intersectionRate>
The fraction of k-mers that needs to be shared by
two intersecting proteins. Should be in range
[0.001,0.1].
--mcl-inflation=<mclInflation>
The MCL inflation. Should be in range [1,19].
(ba
実行方法
1、ゲノムのデータベースを作成する。ゲノムのFASTA形式ファイルのリストファイル(1行に1つずつfastaファイルのパスが書かれたテキスト)を指定する。pantools build_panproteomeコマンドを使う。
#genomeはbuild_pangenomeサブコマンドを使う
ls <path>/<to>/*fasta > genome_list
pantools build_pangenome genomeDB genome_list
#proteomeはbuild_panproteomeサブコマンドを使う
ls <path>/<to>/*faa > proteome_list
pantools build_panproteome proteomeDB -pf proteome_lis
5つの植物のクロロプラストゲノムからパンゲノムを構築するチュートリアルが用意されている。
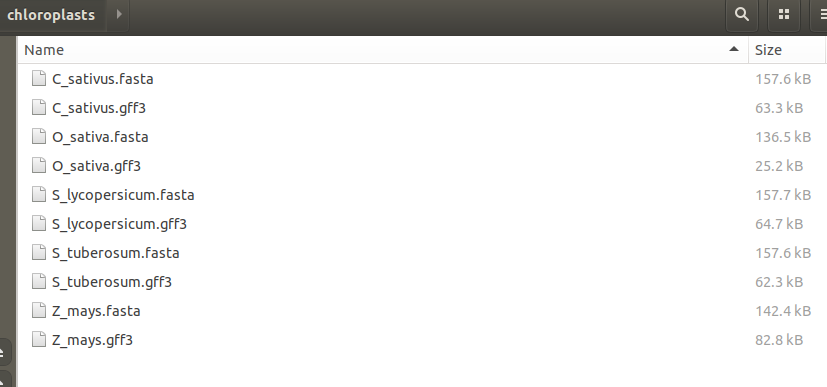 これを試す。リストを作り、実行する。
これを試す。リストを作り、実行する。
> ls *fasta > list #できたリストファイルに空行があるとエラーになる(最終行の末尾に改行があれば消す)
pantools build_pangenomeの実行。作成するD.B名、リストの順に指定する。
> pantools build_pangenome genomeDB genome_list
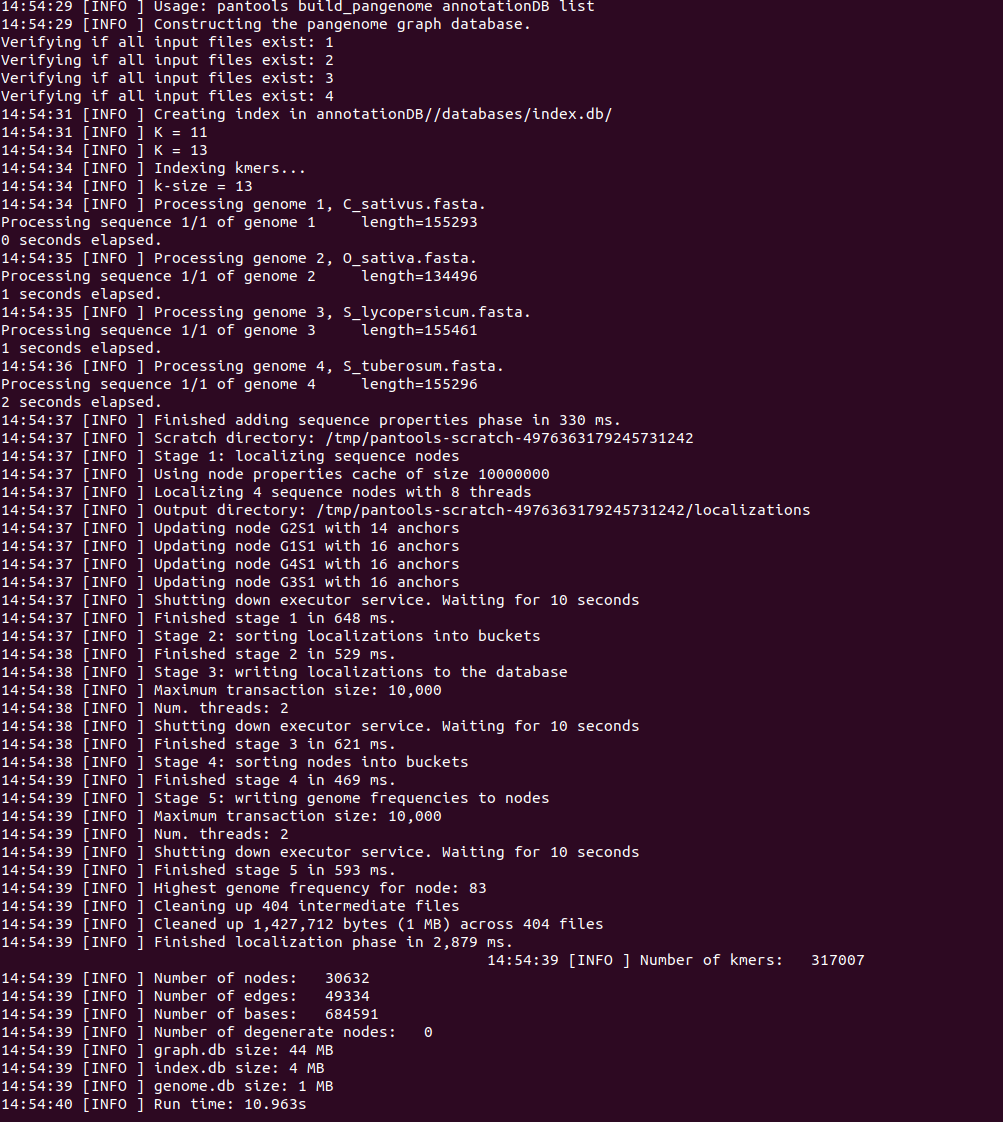
genomeDB/
2、既存のデータベースに追加のファイル(ゲノムDBならゲノム)を追加することもできる。それにはpantools add_genomesコマンドを使う。fastaの代わりにGFF3形式のアノテーション付きファイルを読み込ませて、遺伝子アノテーションもグラフに追加することができる。
ls <path>/<to>/genome*fasta > extra_genome_list
pantools add_genomes genomeDB extra_genome_list
ls <path>/<to>/*GFF3 > GFF3_list
pantools add_annotations --connect genomeDB GFF3_list
ゲノムのパンゲノムD.BにアノテーションのGFF3を追加する場合、どのゲノムに対応するかを番号で指定し、<NUM><single space><name.gff3>としたリストで指定する。

番号はbuild_pangenomeのlog(上の写真の上の方)に書かれている。また、作成したD.Bディレクトリでも確認できる。
準備ができたら実行する。
> pantools add_annotations --connect genomeDB GFF3_list
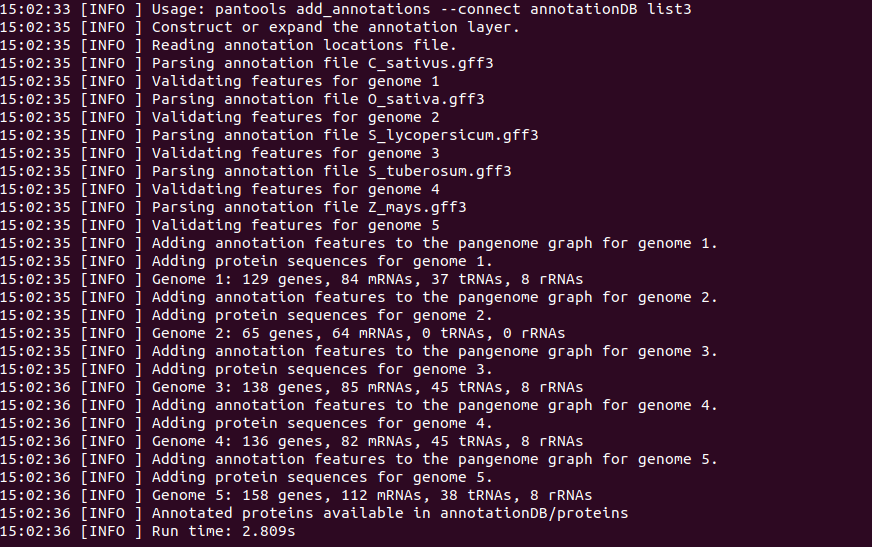
genomeDB/
proteinsディレクトリが追加されている(build_panproteomeでproteomesからD.Bを作っていれば1のコマンド後には存在している)。
3、プロテオームデータベースに表現型情報を記載したCSVファイルを追加して、表現型情報との関係を調べることができる。マニュアルでは、例としてGenome,Gram,Region,Pathogenicity,Boolean,float,speciesが挙げられている。それにはpantools add_phenotypeコマンドを使う。
pantools add_phenotype tomato_DB --phenotype pheno.csv
他にもbuscoの結果を付与したり機能的アノテーションの結果を付与する事ができる。
4、パンゲノムやパンプロテオームの分析を行うには、初めに配列類似度に基づいてタンパク質をグループ分けする必要がある。
pantools group tomato_DB -tn 20 --relaxation 4
- --database-path,-dp Path to the pangenome database.
- --threads, -tn The number of parallel working threads. Default and minimum required threads is 3.
- --relaxation, -rn The relaxation in homology calls. Should be in range [1-8], from strict to relaxed (default 1). IMPORTANT! This argument automatically sets the four remaining arguments, stated here below.
> pantools group genomeDB --relaxation 1

genomeDB/

5、DBから情報を取り出すにはゲノムの座標を指定する。座標の指定は、ゲノムのリストの通し番号、コンティグ名、start、endをスペース区切りで書いたテキストファイルを指定する。
pantools retrieve_regions genome_DB regions.txt
あるゲノムを全部取り出すには、座標を指定せずにゲノムのリストの通し番号だけ指定したテキストを用意する。結果は作成したDBディレクトリ/retrieval/に自動で保存される。
6、Neo4jブラウザでパンゲノムを探索する。
neo4j start
引用
PanTools v3: functional annotation, classification and phylogenomics
Eef M Jonkheer, Dirk-Jan M van Workum, Siavash Sheikhizadeh Anari, Balázs Brankovics, Jorn R de Haan, Lidija Berke, Theo A J van der Lee, Dick de Ridder, Sandra Smit
Bioinformatics, Volume 38, Issue 18, 15 September 2022, Pages 4403–4405