2019 5/7 タイトル修正
トランスファーRNA(tRNA)は、遺伝暗号のタンパク質への翻訳者として働き全ての生物に存在している。 tRNA scan-SE(ref.1)は、ゲノム中のtRNA遺伝子を同定およびアノテーションするための最も広く使用されているツールである。 8000以上の引用があり、そのユーザーはRNA生物学者、シークエンシングセンター、データベースアノテーター、そして他の基礎研究者を含む。 UNIXベースのソフトウェアを扱う専門知識を持たない可能性がある研究者の使いやすさを向上させるために、tRNA scan-SE On-line Webサイト(ref.2、3)には、迅速で詳細なtRNA分析が掲載されている。tRNA scan-SEを使用して予測されたtRNAは、何千ものゲノムについてGenomic tRNAデータベース(GtRNA db)(ref.4、5)で利用可能であり、生命の3つのドメインすべてにわたって高品質のtRNAコレクションを閲覧できる。
オリジナルのtRNA scan-SEの実装は、非常に貴重なRfamデータベース(ref.7)よりも前に、ゲノム内のRNA遺伝子にアノテーションを付けるための共分散モデル(CM)(ref.6)の大規模な使用を開拓した。同じRNAファミリーの構造的にアラインしたメンバーをトレーニングすることにより、共分散モデルは、一次配列と二次構造の両方の情報を統合できるstochastic context-free grammarsを介してRNA保存を捉える。集中的な計算要件にもかかわらず、共分散モデルは、tRNAおよび他の多くの構造化RNAを見出すことにおいて比類のない感度および特異性をもたらす。tRNA共分散モデルとのアラインメントによって、任意の所与の配列からtRNAを検索できる。共分散モデルを構築するために使用されるtRNAのトレーニングセットに応じて、検索は任意のtRNA配列の一般的な検出、またはクレード特異的な特徴を有するtRNAを検出するためのより専門的な検索(例えば真核細胞質型tRNA)または特異的tRNAの種類(例:開始メチオニンtRNA)に利用できる。したがって、tRNA scan-SEは、高品質のトレーニングセットアライメントによってのみ制限され、さまざまな種類のtRNAに対して簡単に「調整」できる。この柔軟性により、以前のバージョンのtRNA scanSで真核生物、バクテリア、アーキア、または細胞小器官のtRNAのクレード固有の検索モードが可能になった。同じ柔軟性は、tRNAシーケンストレーニングセットによってのみ制限される、強力な新しいクレードとアイソタイプ固有の検索モードのためのフレームワークを提供する。全ゲノムにわたるCM検索とアライメントに必要な計算負荷を減らすために、オリジナルのtRNA scan-SEは、推定tRNAを同定するための初回通過スクリーニングとして2つの高速で高感度なアルゴリズムを使用した(ref.8,9)。次にプログラムは推定tRNAのみをCMにアラインメントし、アイソタイプやイントロン境界などの重要な情報を同定した。初期の一般的およびドメイン特異的なCMは、ゴールドスタンダードのSprinzlデータベースから抽出された1,415のtRNAのアライメントを用いて構築され(ref.10、11)、CMの構築およびアライメントはCOVEを用いて行われた(ref.6)。
その最初の実施以来、tRNA遺伝子およびtmRNA遺伝子の両方を検出するARAGORN(ref.12)を含む、他の多数の tRNA検出および分類方法が開発されてきた。 DOGMA(ref.13)、ARWEN(ref.14)、MITOS(ref.15)、およびtRNAファインダー(ref.17)は、さまざまなタイプのオルガネラゲノムのtRNAにアノテーションを付けるために設計されている。 SPLITS(ref.18)は、微生物ゲノム中のスプリットおよびイントロンを含むtRNAを見つけるために設計されている。これらの方法はすべてtRNA scan-SEを改善または補完するように設計されており、特にtRNA scan-SEのコア検出ソフトウェアに依存しているものが多くある。
tRNA scan-SEは、過去20年間tRNA検出のための信頼性が高くアクセスしやすいツールであり続けているが、新しいアルゴリズム、新しいデータ、および性能と機能予測精度の向上のための新しい戦略を組み込むための大きな修正が必要だった。ここでは、次のような機能強化が行われた最新バージョンのtRNA scan-SEについて説明する。(1)Infernal 1.1共分散モデル検索ソフトウェアの統合という形での改良型共分散モデル検索技術(ref.19)。 (2)新たにシーケンシングされた何千ものゲノムからのより広く代表的な多様性のtRNA遺伝子を利用する最新の検索モデル(表1)。 (3)完全な一連のアイソタイプ特異的tRNA共分散モデルからの比較情報に基づくtRNAのより良い機能的分類、および(4)タンパク質で最も使用される可能性が高い真核生物のtRNAを同定するための新しい「高信頼」フィルター翻訳。
インストール
condaで導入できる。macのminiconda3-4.3.30環境でテストした。
mamba install -c bioconda trnascan-se
> tRNAscan-SE -h
$ tRNAscan-SE -h
tRNAscan-SE 2.0 (December 2017)
Copyright (C) 2017 Patricia Chan and Todd Lowe
University of California Santa Cruz
Freely distributed under the GNU General Public License (GPLv3)
Usage: tRNAscan-SE [-options] <FASTA file(s)>
Scan a sequence file for tRNAs
-- default: use Infernal & tRNA covariance models
with eukaryotic sequences
(use 'Search Mode Options' below to scan other types of sequences)
Search Mode Options:
-E : search for eukaryotic tRNAs (default)
-B : search for bacterial tRNAs
-A : search for archaeal tRNAs
-M <model> : search for mitochondrial tRNAs
options: mammal, vert
-O : search for other organellar tRNAs
-G : use general tRNA model (cytoslic tRNAs from all 3 domains included)
--mt <model> : use mito tRNA models for cytosolic/mito detemination
(if not specified, only cytosolic isotype-specific model scan will be performed)
-I : search using Infernal
default use with -E, -B, -A, or -G; optional for -O
--max : maximum sensitivity mode - search using Infernal without hmm filter (very slow)
-L : search using the legacy method (tRNAscan, EufindtRNA, and COVE)
use with -E, -B, -A or -G
-C --cove : search using COVE analysis only (legacy, extremely slow)
default use with -O
-H --breakdown : show breakdown of primary and secondary structure components to
covariance model bit scores
-D --nopseudo : disable pseudogene checking
Output options:
-o --output <file> : save final results in <file>
-f --struct <file> : save tRNA secondary structures to <file>
-s --isospecific <file> : save results using isotype-specific models in <file>
-m --stats <file> : save statistics summary for run in <file>
(speed, # tRNAs found in each part of search, etc)
-b --bed <file> : save results in BED file format of <file>
-a --fasta <file> : save predicted tRNA sequences in FASTA file format of <file>
-l --log <file> : save log of program progress in <file>
--detail : display prediction outputs in detailed view
--brief : brief output format (no column headers)
-? # : '#' in place of <file> chooses default name for output files
-p --prefix <label> : use <label> prefix for all default output file names
-d --progress : display program progress messages
-q --quiet : quiet mode (credits & run option selections suppressed)
-y --hitsrc : show origin of hits (Ts=tRNAscan 1.4, Eu=EufindtRNA,
Bo=Both Ts and Eu, Inf=Infernal)
Specify Alternate Cutoffs / Data Files:
-X --score <score> : set cutoff score (in bits) for reporting tRNAs (default=20)
-g --gencode <file> : use alternate genetic codes specified in <file> for
determining tRNA type
-z --pad <number> : use <number> nucleotides padding when passing first-pass
tRNA bounds predictions to CM analysis (default=8)
--len <length> : set max length of tRNA intron+variable region for legacy search mode
(default=116bp)
Misc Options:
-h --help : print this help message
-c --conf <file> : tRNAscan-SE configuration file (default: tRNAscan-SE.conf)
-Q --forceow : do not prompt user before overwriting pre-existing
result files (for batch processing)
--match <EXPR> : search only sequences with names matching <EXPR> string
(<EXPR> may contain * or ? wildcard chars)
--search <EXPR> : start search at sequence with name matching <EXPR> string
and continue to end of input sequence file(s)
Special Advanced Options (for testing & special purposes)
-U : search for tRNAs with alternate models defined in configuration file
-t --tscan : search using tRNAscan only (defaults to strict params)
--tmode <mode> : explicitly set tRNAscan params, where <mode>=R or S
(R=relaxed, S=strict tRNAscan v1.3 params)
-v --verbose <file> : save verbose tRNAscan 1.3 output to <file>
--nomerge : Keep redundant tRNAscan 1.3 hits (don't filter out multiple
predictions per tRNA identification)
-e --eufind : search using Eukaryotic tRNA finder (EufindtRNA) only
(defaults to Normal seach parameters when run alone,
or to Relaxed search params when run with Cove)
--emode <mode> : explicitly set EufindtRNA params, where <mode>=R, N, or S
(relaxed, normal, or strict)
--iscore <score> : manually set "intermediate" cutoff score for EufindtRNA
-r --fsres <file> : save first-pass scan results from EufindtRNA, tRNAscan, or
Infernal hmm in <file> in tabular results format
--mid : fast scan mode - search using Infernal with mid-level strictness of hmm filter
-F --falsepos <file> : save first-pass candidate tRNAs in <file> that were then
found to be false positives by second-pass analysis
--missed <file> : save all seqs that do NOT have at least one
tRNA prediction in them (aka "missed" seqs)
--thread <number> : number of threads used for running infernal (default is to use available threads)
実行方法
genomeのfastaかraw fastqを選択する。
tRNAscan-SE input_genome.fa -o output
- -E search for eukaryotic tRNAs (default)
- -B search for bacterial tRNAs
- -A search for archaeal tRNAs
- -M <model> : search for mitochondrial tRNAs
- -O search for other organellar tRNAs
- -o save final results in <file>
web版の使い方
http://trna.ucsc.edu/tRNAscan-SE/にアクセスする。
Downloadからはソースコードをダウンロードできる。
Sequence sourceから種を選択する。各検索モードは選択された種または系統発生グループからのtRNAトレーニングデータに基づいている。

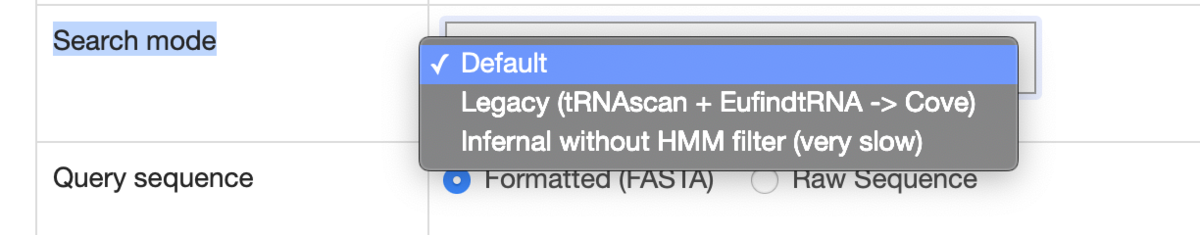
Search modeから使用する確率モデルを選択する。標準の検索モードはほとんどの場合高速で十分にsensitiveだが、極端に異なるtRNAを含むショートリードの場合、「Infernal without HMM filter」モードにするとわずかに感度が向上する。
ファイルを選択ボタンから、ゲノム配列のfasta、またはraw fastqを指定する。

必要に応じてadvanced user向けパラメータを設定する。

Run tRNAscan-SEボタンを押して検索を実行する。
検出されたtRNAが表示される。

予測された各tRNAは、アイソタイプ特異的モデルでさらに評価される。

最後にRun statisticsがまとめられる。




引用
tRNAscan-SE 2.0: Improved Detection and Functional Classification of Transfer RNA Genes
Patricia P. Chan, Brian Y. Lin, Allysia J. Mak, Todd M. Lowe
bioRxiv preprint first posted online Apr. 30, 2019
関連
