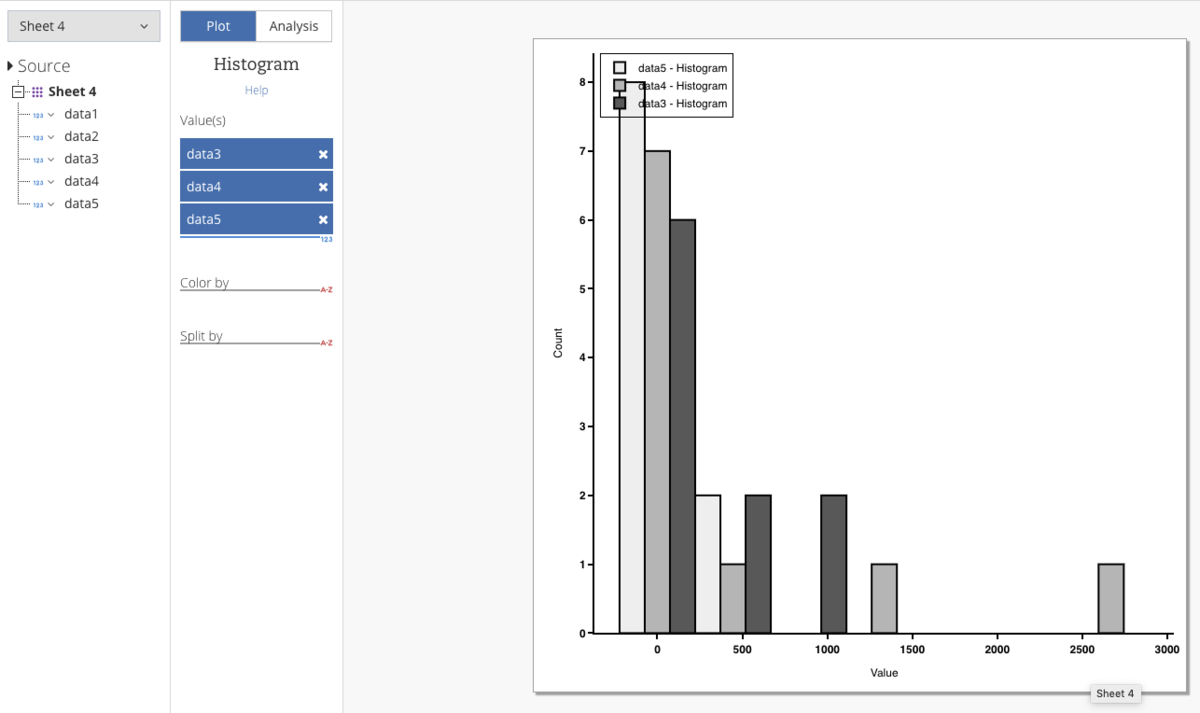
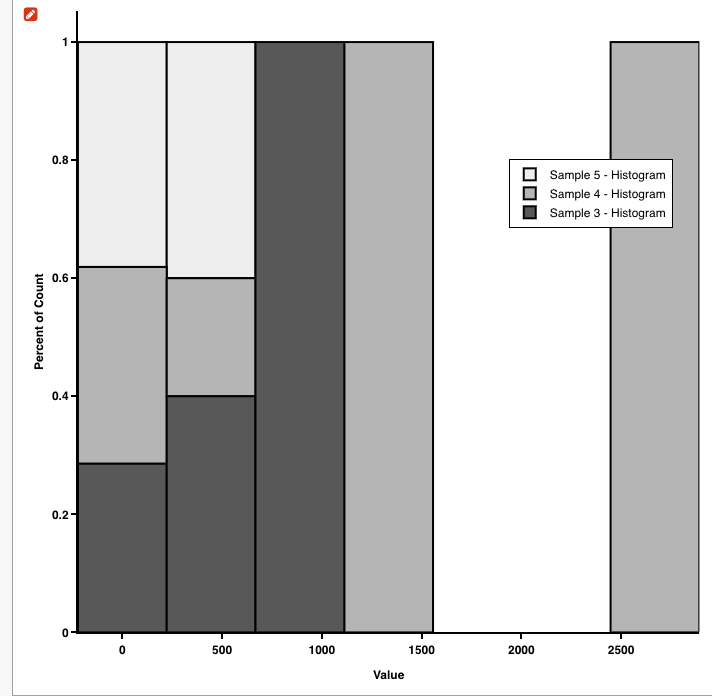
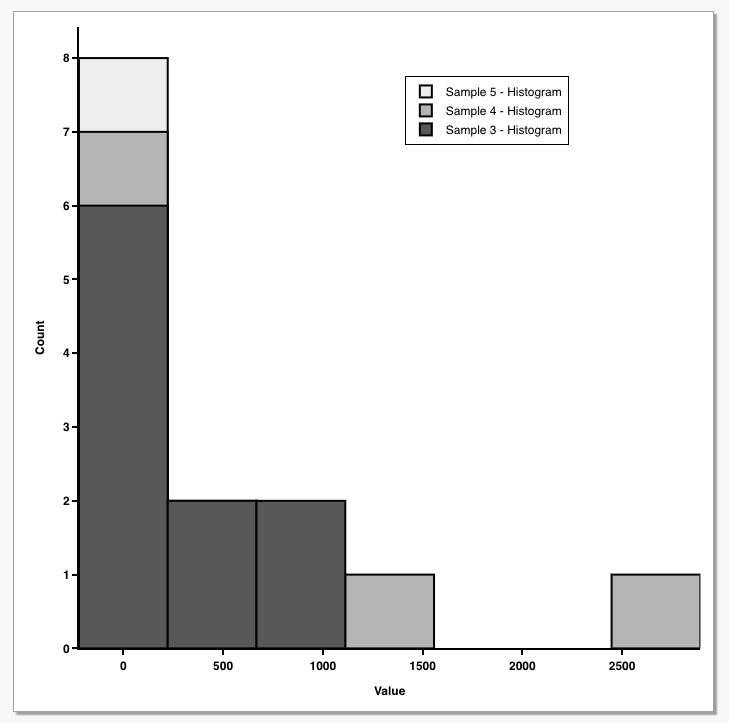
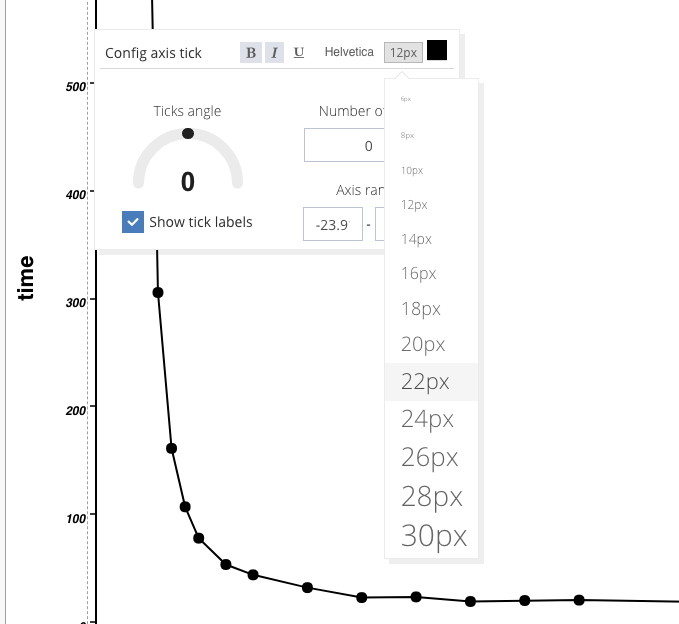
2020 4/22 追記
2020 5/20 コード修正
ハイスループットシーケンシングとオミックス技術の進歩は、自然界に存在する微生物群集の研究に革命をもたらしている。微生物のライフスタイルを包括的に調査するためには、遺伝情報を対話的に整理して可視化し、複雑なデータの分解能を高めるための微妙な違いを取り入れる能力が必要となる。ここでは、複数のソースからのオミックスデータを単一の直感的な表現にリンクすることができるインタラクティブなインターフェースを備えた、メタゲノムアセンブリ内の微生物ゲノムの自動化とヒト主導の特性評価を提供する先進的な解析および可視化プラットフォームであるanvi'oを紹介する。その拡張可能な可視化アプローチは、各コンティグに関する多次元の情報を抽出し、データの探索、操作、報告のためのダイナミックで統一された作業環境を提供する。Anvi'oを使用して、公開されているデータセットを再解析し、1塩基変異のデノボの特徴付けを通じて、微生物集団内のゲノムの時間的変化を探り、培養種やシングルセルゲノムをメタゲノムやメタトランスクリプトームデータとリンクさせた。Anvi'oは、広範なバイオインフォマティクスのスキルを持たない研究者でも、大規模な「オミックスデータセット」の詳細な分析を実行し、伝えることができるようにするオープンソースのプラットフォームである。
HP
http://merenlab.org/software/anvio/
Anvi'oを使用すると、メタゲノムのビニング、一塩基変異の分析、バクテリアパンゲノムの研究、メタゲノムアセンブリ内のバクテリアゲノム数予測、また真核生物アセンブリプロジェクトからの汚染の除去までを行うことができる。
積極的なバージョンアップによって機能も徐々に変わってきています。注意して使って下さい。
インストール
公式dockerイメージを使って複数のubuntu18.04LTSマシンでテストした。
本体 Github
#bioconda (link)注意;依存が多いため時間がかかる
conda create -n anvio -y
conda activate anvio
conda install -c bioconda anvio -y
#homebrew (not tested)
brew tap merenlab/anvio
brew install merenlab/anvio/anvio
テスト
> anvi-self-test --suite mini
#依存が多いので、condaだと依存チェックに異常な時間がかかる。動かすだけならdockerが楽。
#latest
docker pull meren/anvio:latest
#lauch
docker run --rm -it -v `pwd`:`pwd` -w `pwd` -p 8080:8080 meren/anvio:latest
> anvi-setup-ncbi-cogs -h
> anvi-setup-ncbi-cogs -h
usage: anvi-setup-ncbi-cogs [-h] [--cog-data-dir COG_DATA_DIR] [--reset]
[--just-do-it] [-T NUM_THREADS]
Download and setup NCBI's Clusters of Orthologous Groups database.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--cog-data-dir COG_DATA_DIR
The directory for COG data to be stored. If you leave
it as is without specifying anything, the default
destination for the data directory will be used to set
things up. The advantage of it is that everyone will
be using a single data directory, but then you may
need superuser privileges to do it. Using this
parameter you can choose the location of the data
directory somewhere you like. However, when it is time
to run COGs, you will need to remember that path and
provide it to the program.
--reset Remove all the previously stored files and start over.
If something is feels wrong for some reason and if you
believe re-downloading files and setting them up could
address the issue, this is the flag that will tell
anvi'o to act like a real computer scientist
challenged with a computational problem.
--just-do-it Don't bother me with questions or warnings, just do
it.
-T NUM_THREADS, --num-threads NUM_THREADS
Maximum number of threads to use for multithreading
whenever possible. Very conservatively, the default is
1. It is a good idea to not exceed the number of CPUs
/ cores on your system. Plus, please be careful with
this option if you are running your commands on a SGE
--if you are clusterizing your runs, and asking for
multiple threads to use, you may deplete your
resources very fast.
> anvi-gen-contigs-database -h
> anvi-gen-contigs-database -h
usage: anvi-gen-contigs-database [-h] -f FASTA [-n PROJECT_NAME]
[-o DB_FILE_PATH] [--description TEXT_FILE]
[-L INT] [-K INT] [--skip-gene-calling]
[--prodigal-translation-table INT]
[--external-gene-calls GENE-CALLS]
[--ignore-internal-stop-codons]
[--skip-mindful-splitting]
Generate a new anvi'o contigs database.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
MANDATORY INPUTS:
Things you really need to provide to be in business.
-f FASTA, --contigs-fasta FASTA
The FASTA file that contains reference sequences you
mapped your samples against. This could be a reference
genome, or contigs from your assembler. Contig names
in this file must match to those in other input files.
If there is a problem anvi'o will gracefully complain
about it.
-n PROJECT_NAME, --project-name PROJECT_NAME
Name of the project. Please choose a short but
descriptive name (so anvi'o can use it whenever she
needs to name an output file, or add a new table in a
database, or name her first born).
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
Things you may want to tweak.
-o DB_FILE_PATH, --output-db-path DB_FILE_PATH
Output file path for the new database.
--description TEXT_FILE
A plain text file that contains some description about
the project. You can use Markdwon syntax. The
description text will be rendered and shown in all
relevant interfaces, including the anvi'o interactive
interface, or anvi'o summary outputs.
-L INT, --split-length INT
Anvi'o splits very long contigs into smaller pieces,
without actually splitting them for real. These
'virtual' splits improve the efficacy of the
visualization step, and changing the split size gives
freedom to the user to adjust the resolution of their
display when necessary. The default value is (20000).
If you are planning to use your contigs database for
metagenomic binning, we advise you to not go below
10,000 (since the lower the split size is, the more
items to show in the display, and decreasing the split
size does not really help much to binning). But if you
are thinking about using this parameter for ad hoc
investigations other than binning, you should ignore
our advice, and set the split size as low as you want.
If you do not want your contigs to be split, you can
set the split size to '0' or any other negative
integer (lots of unnecessary freedom here, enjoy!).
-K INT, --kmer-size INT
K-mer size for k-mer frequency calculations. The
default k-mer size for composition-based analyses is
4, historically. Although tetra-nucleotide frequencies
seem to offer the the sweet spot of sensitivity,
information density, and manageable number of
dimensions for clustering approaches, you are welcome
to experiment (but maybe you should leave it as is for
your first set of analyses).
--skip-mindful-splitting
By default, anvi'o attempts to prevent soft-splitting
large contigs by cutting proper gene calls to make
sure a single gene is not broken into multiple splits.
This requires a careful examination of where genes
start and end, and to find best locations to split
contigs with respect to this information. So, when the
user asks for a split size of, say, 1,000, it serves
as a mere suggestion. When this flag is used, anvi'o
does what the user wants and creates splits at desired
lengths (although some functionality may become
unavailable for the projects that rely on a contigs
database that is initiated this way).
GENES IN CONTIGS:
Expert thingies.
--skip-gene-calling By default, generating an anvi'o contigs database
includes the identification of open reading frames in
contigs by running a bacterial gene caller. Declaring
this flag will by-pass that process. If you prefer,
you can later import your own gene calling results
into the database.
--prodigal-translation-table INT
This is a parameter to pass to the Prodigal for a
specific translation table. This parameter corresponds
to the parameter `-g` in Prodigal, the default value
of which is 11 (so if you do not set anything, it will
be set to 11 in Prodigal runtime. Please refer to the
Prodigal documentation to determine what is the right
translation table for you if you think you need it.)
--external-gene-calls GENE-CALLS
A TAB-delimited file to utilize external gene calls.
The file must have these columns: 'gene_callers_id' (a
unique integer number for each gene call, start from
1), 'contig' (the contig name the gene call is found),
'start' (start position, integer), 'stop' (stop
position, integer), 'direction' (the direction of the
gene open reading frame; can be 'f' or 'r'), 'partial'
(whether it is a complete gene call, or a partial one;
must be 1 for partial calls, and 0 for complete
calls), 'source' (the gene caller), and 'version' (the
version of the gene caller, i.e., v2.6.7 or v1.0). An
example file can be found via the URL
--ignore-internal-stop-codons
This is only relevant when you have an external gene
calls file. If anvi'o figures out that your custom
gene calls result in amino acid sequences with stop
codons in the middle, it will complain about it. You
can use this flag to tell anvi'o to don't check for
internal stop codons, EVEN THOUGH IT MEANS THERE IS
MOST LIKELY SOMETHING WRONG WITH YOUR EXTERNAL GENE
CALLS FILE. Anvi'o will understand that sometimes we
don't want to care, and will not judge you. Instead,
it will replace every stop codon residue in the amino
acid sequence with an 'X' character. Please let us
know if you used this and things failed, so we can
tell you that you shouldn't have really used it if you
didn't like failures at the first place (smiley).
> anvi-run-hmms -h
> anvi-run-hmms -h
usage: anvi-run-hmms [-h] -c CONTIGS_DB [-H HMM PROFILE PATH]
[-I HMM PROFILE NAME] [--also-scan-trnas]
[-T NUM_THREADS] [--just-do-it]
This program deals with populating tables that store HMM hits in an anvi'o
contigs database.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
DB:
An anvi'o contigs adtabase to populate with HMM hits
-c CONTIGS_DB, --contigs-db CONTIGS_DB
Anvi'o contigs database generated by 'anvi-gen-
contigs'
HMM OPTIONS:
If you have your own HMMs, or if you would like to run only a set of
default anvi'o HMM profiles rather than running them all, this is your
stop.
-H HMM PROFILE PATH, --hmm-profile-dir HMM PROFILE PATH
You can use this parameter you can specify a directory
path that contain an HMM profile. This way you can run
HMM profiles that are not included in anvi'o. See the
online to find out about the specifics of this
directory structure .
-I HMM PROFILE NAME, --installed-hmm-profile HMM PROFILE NAME
When you run this program without any parameter, it
runs all 4 HMM profiles installed on your system. If
you want only a specific one to run, you can select it
by using this parameter. These are the currently
available ones: "Protista_83" (type: singlecopy),
"Bacteria_71" (type: singlecopy), "Archaea_76" (type:
singlecopy), "Ribosomal_RNAs" (type: Ribosomal_RNAs).
tRNAs:
Through this program you can also scan Transfer RNA sequences in your
contigs database for free (instead of running `anvi-scan-trnas` later).
--also-scan-trnas Also scan tRNAs while you're at it.
PERFORMANCE:
Stuff everyone forgets to set and then get upset with how slow science
goes.
-T NUM_THREADS, --num-threads NUM_THREADS
Maximum number of threads to use for multithreading
whenever possible. Very conservatively, the default is
1. It is a good idea to not exceed the number of CPUs
/ cores on your system. Plus, please be careful with
this option if you are running your commands on a SGE
--if you are clusterizing your runs, and asking for
multiple threads to use, you may deplete your
resources very fast.
AUTHORITY:
Because you are the boss.
--just-do-it Don't bother me with questions or warnings, just do
it.
> anvi-display-contigs-stats -h
> anvi-display-contigs-stats -h
usage: anvi-display-contigs-stats [-h] [--report-as-text] [-o FILE_PATH]
[-I IP_ADDR] [-P INT] [--browser-path PATH]
[--server-only] [--password-protected]
CONTIG DATABASES) [CONTIG DATABASE(S ...]
Start the anvi'o interactive interactive for viewing or comparing contigs
statistics
positional arguments:
CONTIG DATABASE(S) Anvio'o Contig databases to display statistics, you
can give multiple databases by seperating them with
space.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
REPORT CONFIGURATION:
Specify what kind of output you want.
--report-as-text If you give this flag, Anvi'o will not open new
browser to show Contigs database statistics and write
all stats to TAB separated file and you should also
give --output-file with this flag otherwise Anvi'o
will complain.
-o FILE_PATH, --output-file FILE_PATH
File path to store results.
SERVER CONFIGURATION:
For power users.
-I IP_ADDR, --ip-address IP_ADDR
IP address for the HTTP server. The default ip address
(0.0.0.0) should work just fine for most.
-P INT, --port-number INT
Port number to use for anvi'o services. If nothing is
declared, anvi'o will try to find a suitable port
number, starting from the default port number, 8080.
--browser-path PATH By default, anvi'o will use your default browser to
launch the interactive interface. If you would like to
use something else than your system default, you can
provide a full path for an alternative browser using
this parameter, and hope for the best. For instance we
are using this parameter to call Google's experimental
browser, Canary, which performs better with demanding
visualizations.
--server-only The default behavior is to start the local server, and
fire up a browser that connects to the server. If you
have other plans, and want to start the server without
calling the browser, this is the flag you need.
--password-protected If this flag is set, command line tool will ask you to
enter a password and interactive interface will be
only accessible after entering same password. This
option is recommended for shared machines like
clusters or shared networks where computers are not
isolated.
> anvi-run-ncbi-cogs -h
> anvi-run-ncbi-cogs -h
usage: anvi-run-ncbi-cogs [-h] -c CONTIGS_DB [--cog-data-dir COG_DATA_DIR]
[-T NUM_THREADS] [--sensitive]
[--temporary-dir-path PATH]
[--search-with SEARCH_METHOD]
Run NCBI's COGs to associate genes in an anvi'o contigs database with
functions. COGs database was been designed as an attempt to classify proteins
from completely sequenced genomes on the basis of the orthology concept. It is
no longer actively developed, however, it is still very effective for daily
needs. You may want to consider Pfams or the eggNOG database for more
comprehensive functional insights.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-c CONTIGS_DB, --contigs-db CONTIGS_DB
Anvi'o contigs database generated by 'anvi-gen-
contigs'
--cog-data-dir COG_DATA_DIR
The directory path for your COG setup. Anvi'o will try
to use the default path if you do not specify
anything.
-T NUM_THREADS, --num-threads NUM_THREADS
Maximum number of threads to use for multithreading
whenever possible. Very conservatively, the default is
1. It is a good idea to not exceed the number of CPUs
/ cores on your system. Plus, please be careful with
this option if you are running your commands on a SGE
--if you are clusterizing your runs, and asking for
multiple threads to use, you may deplete your
resources very fast.
--sensitive DIAMOND sensitivity. With this flag you can instruct
DIAMOND to be 'sensitive', rather than 'fast' during
the search. It is likely the search will take
remarkably longer. But, hey, if you are doing it for
your final analysis, maybe it should take longer and
be more accurate. This flag is only relevant if you
are running DIAMOND.
--temporary-dir-path PATH
If you don't provide anything here, this program will
come up with a temporary directory path by itself to
store intermediate files, and clean it later. If you
want to have full control over this, you can use this
flag to define one..
--search-with SEARCH_METHOD
What program to use for database searching. The
default search uses diamond. All available options
include: diamond, blastp.
> anvi-get-sequences-for-gene-calls -h
> anvi-get-sequences-for-gene-calls -h
usage: anvi-get-sequences-for-gene-calls [-h] [-c CONTIGS_DB]
[--gene-caller-ids GENE_CALLER_IDS]
[--delimiter CHAR]
[--report-extended-deflines]
[--wrap WRAP] [--export-gff3]
[--get-aa-sequences]
[-g GENOMES_STORAGE]
[-G GENOME_NAMES] -o FILE_PATH
A script to get back sequences for gene calls
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
OPTION #1: EXPORT FROM CONTIGS DB:
-c CONTIGS_DB, --contigs-db CONTIGS_DB
Anvi'o contigs database generated by 'anvi-gen-
contigs'
--gene-caller-ids GENE_CALLER_IDS
Gene caller ids. Multiple of them can be declared
separated by a delimiter (the default is a comma). In
anvi-gen-variability-profile, if you declare nothing
you will get all genes matching your other filtering
criteria. In other programs, you may get everything,
nothing, or an error. It really depends on the
situation. Fortunately, mistakes are cheap, so it's
worth a try.
--delimiter CHAR The delimiter to parse multiple input terms. The
default is ','.
--report-extended-deflines
When declared, the deflines in the resulting FASTA
file will contain more information.
--wrap WRAP When to wrap sequences when storing them in a FASTA
file. The default is '120'. A value of '0' would be
equivalent to 'do not wrap'.
--export-gff3 If this is true, the output file will be in GFF3
format.
--get-aa-sequences Store amino acid sequences instead.
OPTION #2: EXPORT FROM A GENOMES STORAGE:
-g GENOMES_STORAGE, --genomes-storage GENOMES_STORAGE
Anvi'o genomes storage file
-G GENOME_NAMES, --genome-names GENOME_NAMES
Genome names to 'focus'. You can use this parameter to
limit the genomes included in your analysis. You can
provide these names as a comma-separated list of
names, or you can put them in a file, where you have a
single genome name in each line, and provide the file
path.
OPTIONS COMMON TO ALL INPUTS:
-o FILE_PATH, --output-file FILE_PATH
File path to store results.
> anvi-import-taxonomy-for-genes -h
> anvi-import-taxonomy-for-genes -h
usage: anvi-import-taxonomy-for-genes [-h] -c CONTIGS_DB [-p PARSER] -i FILES)
[FILE(S ...] [--just-do-it]
Import gene-level taxonomy into an anvi'o contigs database.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-c CONTIGS_DB, --contigs-db CONTIGS_DB
Anvi'o contigs database generated by 'anvi-gen-
contigs'
-p PARSER, --parser PARSER
Parser to make sense of the input files. There are 3
parsers readily available: ['default_matrix',
'centrifuge', 'kaiju']. It is OK if you do not select
a parser, but in that case there will be no additional
contigs available except the identification of single-
copy genes in your contigs for later use. Using a
parser will not prevent the analysis of single-copy
genes, but make anvio more powerful to help you make
sense of your results. Please see the documentation,
or get in touch with the developers if you have any
questions regarding parsers.
-i FILE(S) [FILE(S) ...], --input-files FILE(S) [FILE(S) ...]
Input file(s) for selected parser. Each parser (except
"blank") requires input files to process that you
generate before running anvio. Please see the
documentation for details.
--just-do-it Don't bother me with questions or warnings, just do
it.
> anvi-merge -h
> anvi-merge -h
usage: anvi-merge [-h] -c CONTIGS_DB [-o DIR_PATH] [-S NAME]
[--description TEXT_FILE] [--skip-hierarchical-clustering]
[--enforce-hierarchical-clustering]
[--distance DISTANCE_METRIC] [--linkage LINKAGE_METHOD] [-W]
SINGLE_PROFILES) [SINGLE_PROFILE(S ...]
Merge multiple anvio profiles
positional arguments:
SINGLE_PROFILE(S) Anvo'o single profiles to merge
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-c CONTIGS_DB, --contigs-db CONTIGS_DB
Anvi'o contigs database generated by 'anvi-gen-
contigs'
-o DIR_PATH, --output-dir DIR_PATH
Directory path for output files
-S NAME, --sample-name NAME
It is important to set a sample name (using only ASCII
letters and digits and without spaces) that is unique
(considering all others). If you do not provide one,
anvi'o will try to make up one for you based on other
information, although, you should never let the
software to decide these things).
--description TEXT_FILE
A plain text file that contains some description about
the project. You can use Markdwon syntax. The
description text will be rendered and shown in all
relevant interfaces, including the anvi'o interactive
interface, or anvi'o summary outputs.
--skip-hierarchical-clustering
If you are not planning to use the interactive
interface (or if you have other means to add a tree of
contigs in the database) you may skip the step where
hierarchical clustering of your items are preformed
based on default clustering recipes matching to your
database type.
--enforce-hierarchical-clustering
If you have more than 25,000 splits in your merged
profile, anvi-merge will automatically skip the
hierarchical clustering of splits (by setting --skip-
hierarchical-clustering flag on). This is due to the
fact that computational time required for hierarchical
clustering increases exponentially with the number of
items being clustered. Based on our experience we
decided that 25,000 splits is about the maximum we
should try. However, this is not a theoretical limit,
and you can overwrite this heuristic by using this
flag, which would tell anvi'o to attempt to cluster
splits regardless.
--distance DISTANCE_METRIC
The distance metric for the hierarchical clustering.
If you do not use this flag, the default distance
metric will be used for each clustering configuration
which is "euclidean".
--linkage LINKAGE_METHOD
The same story with the `--distance`, except, the
system default for this one is ward.
-W, --overwrite-output-destinations
Overwrite if the output files and/or directories
exist.
> anvi-profile -h
> anvi-profile -h
usage: anvi-profile [-h] [-i INPUT_BAM] [-c CONTIGS_DB] [--blank-profile]
[-o DIR_PATH] [-W] [-S NAME] [--report-variability-full]
[--skip-SNV-profiling] [--profile-SCVs]
[--description TEXT_FILE] [--cluster-contigs]
[--skip-hierarchical-clustering]
[--distance DISTANCE_METRIC] [--linkage LINKAGE_METHOD]
[-M INT] [--max-contig-length INT] [-X INT] [-V INT]
[--list-contigs] [--contigs-of-interest FILE]
[-T NUM_THREADS] [--queue-size INT]
[--write-buffer-size-per-thread INT] [--force-multi]
Creates a single anvi'o profile database. The default input to this program is
a BAM file. When it is run on a BAM file, depending on the user parameters,
the program quantifies coverage per nucleotide position (and averages them out
per contig), calculates single-nucleotide, single-codon, and single-amino acid
variants, and stores these data into appropriate tables. Anvi'o single
profiles can be merged by the program `anvi-merge`.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
INPUTS:
There are two possible inputs for anvio profiler. You must to declare
either of these two.
-i INPUT_BAM, --input-file INPUT_BAM
Sorted and indexed BAM file to analyze. Takes a long
time depending on the length of the file and
parameters used for profiling.
-c CONTIGS_DB, --contigs-db CONTIGS_DB
Anvi'o contigs database generated by 'anvi-gen-
contigs'
--blank-profile If you only have contig sequences, but no mapping data
(i.e., you found a genome and would like to take a
look from it), this flag will become very hand. After
creating a contigs database for your contigs, you can
create a blank anvi'o profile database to use anvi'o
interactive interface with that contigs database
without any mapping data.
EXTRAS:
Things that are not mandatory, but can be useful if/when declared.
-o DIR_PATH, --output-dir DIR_PATH
Directory path for output files
-W, --overwrite-output-destinations
Overwrite if the output files and/or directories
exist.
-S NAME, --sample-name NAME
It is important to set a sample name (using only ASCII
letters and digits and without spaces) that is unique
(considering all others). If you do not provide one,
anvi'o will try to make up one for you based on other
information, although, you should never let the
software to decide these things).
--report-variability-full
One of the things anvi-profile does is to store
information about variable nucleotide positions.
Usually it does not report every variable position,
since not every variable position is genuine
variation. Say, if you have 1,000 coverage, and all
nucleotides at that position are Ts and only one of
them is a C, the confidence of that C being a real
variation is quite low. anvi'o has a simple algorithm
in place to reduce the impact of noise. However, using
this flag you can disable it and ask profiler to
report every single variation (which may result in
very large output files and millions of reports, but
you are the boss). Do not forget to take a look at '--
min-coverage-for-variability' parameter
--skip-SNV-profiling By default, anvi'o characterizes single-nucleotide
variation in each sample. The use of this flag will
instruct profiler to skip that step. Please remember
that parameters and flags must be identical between
different profiles using the same contigs database for
them to merge properly.
--profile-SCVs Anvi'o can perform accurate characterization of codon
frequencies in genes during profiling. While having
codon frequencies opens doors to powerful evolutionary
insights in downstream analyses, due to its
computational complexity, this feature comes 'off' by
default. Using this flag you can rise against the
authority, as you always should, and make anvi'o
profile codons.
--description TEXT_FILE
A plain text file that contains some description about
the project. You can use Markdwon syntax. The
description text will be rendered and shown in all
relevant interfaces, including the anvi'o interactive
interface, or anvi'o summary outputs.
HIERARCHICAL CLUSTERING:
Do you want your splits to be clustered? Yes? No? Maybe? Remember: By
default, anvi-profile will not perform hierarchical clustering on your
splits; but if you use `--blank` flag, it will try. You can skip that by
using the `--skip-hierarchical-clustering` flag.
--cluster-contigs Single profiles are rarely used for genome binning or
visualization, and since clustering step increases the
profiling runtime for no good reason, the default
behavior is to not cluster contigs for individual
runs. However, if you are planning to do binning on
one sample, you must use this flag to tell anvi'o to
run cluster configurations for single runs on your
sample.
--skip-hierarchical-clustering
If you are not planning to use the interactive
interface (or if you have other means to add a tree of
contigs in the database) you may skip the step where
hierarchical clustering of your items are preformed
based on default clustering recipes matching to your
database type.
--distance DISTANCE_METRIC
The distance metric for the hierarchical clustering.
Only relevant if you are using `--cluster-contigs`
flag. The default is "euclidean".
--linkage LINKAGE_METHOD
The linkage method for the hierarchical clustering.
Just like the distance metric this is only relevant if
you are using it with `--cluster-contigs` flag. The
default is "ward".
NUMBERS:
Defaults of these parameters will impact your analysis. You can always
come back to them and update your profiles, but it is important to make
sure defaults are reasonable for your sample.
-M INT, --min-contig-length INT
Minimum length of contigs in a BAM file to analyze.
The minimum length should be long enough for tetra-
nucleotide frequency analysis to be meaningful. There
is no way to define a golden number of minimum length
that would be applicable to genomes found in all
environments, but we chose the default to be 1000, and
have been happy with it. You are welcome to
experiment, but we advise to never go below 1,000. You
also should remember that the lower you go, the more
time it will take to analyze all contigs. You can use
--list-contigs parameter to have an idea how many
contigs would be discarded for a given M.
--max-contig-length INT
Just like the minimum contig length parameter, but to
set a maximum. Basically this will remove any contig
longer than a certain value. Why would anyone need
this? Who knows. But if you ever do, it is here.
-X INT, --min-mean-coverage INT
Minimum mean coverage for contigs to be kept in the
analysis. The default value is 0, which is for your
best interest if you are going to profile multiple BAM
files which are then going to be merged for a cross-
sectional or time series analysis. Do not change it if
you are not sure this is what you want to do.
-V INT, --min-coverage-for-variability INT
Minimum coverage of a nucleotide position to be
subjected to SNV profiling. By default, anvi'o will
not attempt to make sense of variation in a given
nucleotide position if it is covered less than 10X.
You can change that minimum using this parameter.
CONTIGS:
Sweet parameters of convenience
--list-contigs When declared, the program will list contigs in the
BAM file and exit gracefully without any further
analysis.
--contigs-of-interest FILE
It is possible to analyze only a group of contigs from
a given BAM file. If you provide a text file, in which
every contig of interest is listed line by line, the
profiler would engine only on those contigs in the BAM
file and ignore the rest. This can be used for
debugging purposes, or to engine on a particular group
of contigs that were identified as relevant during the
interactive analysis.
PERFORMANCE:
Performance settings for profiler
-T NUM_THREADS, --num-threads NUM_THREADS
Maximum number of threads to use for multithreading
whenever possible. Very conservatively, the default is
1. It is a good idea to not exceed the number of CPUs
/ cores on your system. Plus, please be careful with
this option if you are running your commands on a SGE
--if you are clusterizing your runs, and asking for
multiple threads to use, you may deplete your
resources very fast.
--queue-size INT The queue size for worker threads to store data to
communicate to the main thread. The default is set by
the class based on the number of threads. If you have
*any* hesitation about whether you know what you are
doing, you should not change this value.
--write-buffer-size-per-thread INT
How many items should be kept in memory before they
are written do the disk. The default is 500 per
thread. So a single-threaded job would have a write
buffer size of 500, whereas a job with 4 threads would
have a write buffer size of 4*500. The larger the
buffer size, the less frequent the program will access
to the disk, yet the more memory will be consumed
since the processed items will be cleared off the
memory only after they are written to the disk. The
default buffer size will likely work for most cases.
Please keep an eye on the memory usage output to make
sure the memory use never exceeds the size of the
physical memory.
--force-multi This is not useful to non-developers. It forces the
multi-process routine even when 1 thread is chosen.
> anvi-interactive -h
> anvi-interactive -h
usage: anvi-interactive [-h] [-p PROFILE_DB] [-c CONTIGS_DB]
[-C COLLECTION_NAME] [--manual-mode] [-f FASTA]
[-d VIEW_DATA] [-t NEWICK] [--items-order FLAT_FILE]
[-V ADDITIONAL_VIEW] [-A ADDITIONAL_LAYERS]
[--gene-mode] [--inseq-stats] [-b BIN_NAME]
[--view NAME] [--title NAME]
[--taxonomic-level {t_domain,t_phylum,t_class,t_order,t_family,t_genus,t_species}]
[--split-hmm-layers] [--hide-outlier-SNVs]
[--state-autoload NAME] [--collection-autoload NAME]
[--export-svg FILE_PATH] [--show-views]
[--skip-check-names] [-o DIR_PATH] [--dry-run]
[--show-states] [--list-collections]
[--skip-init-functions] [--skip-auto-ordering]
[--distance DISTANCE_METRIC]
[--linkage LINKAGE_METHOD] [-I IP_ADDR] [-P INT]
[--browser-path PATH] [--read-only] [--server-only]
[--password-protected] [--user-server-shutdown]
Start an anvi'o server for the interactive interface
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
DEFAULT INPUTS:
The interavtive interface can be started with and without anvi'o
databases. The default use assumes you have your profile and contigs
database, however, it is also possible to start the interface using ad hoc
input files. See 'MANUAL INPUT' section for required parameters.
-p PROFILE_DB, --profile-db PROFILE_DB
Anvi'o profile database
-c CONTIGS_DB, --contigs-db CONTIGS_DB
Anvi'o contigs database generated by 'anvi-gen-
contigs'
-C COLLECTION_NAME, --collection-name COLLECTION_NAME
If you have a collection in your profile database, you
can use this flag to start the interactive interface
with a tree showing your bins in your collection,
instead of each split. This is very useful when you
have imported your external binning results into
anvi'o, and want to see the distribution of your bins
across samples. In these cases anvi'o will cluster
your bins and based on multiple metrics. Because this
particular clustering will be done on the fly within
anvi'o interactive class, you get to define a
disntance metric and a linkage method using --linkage
and --distance parameters if you want!
MANUAL INPUTS:
Mandatory input parameters to start the interactive interface without
anvi'o databases.
--manual-mode Using this flag, you can run the interactive interface
in an ad hoc manner using input files you curated
instead of standard output files generated by an
anvi'o run. In the manual mode you will be asked to
provide a profile database. In this mode a profile
database is only used to store 'state' of the
interactive interface so you can reload your visual
settings when you re-analyze the same files again. If
the profile database you provide does not exist,
anvi'o will create an empty one for you.
A FASTA-formatted input file
-d VIEW_DATA, --view-data VIEW_DATA
A TAB-delimited file for view data
-t NEWICK, --tree NEWICK
NEWICK formatted tree structure
--items-order FLAT_FILE
A flat file that contains the order of items you wish
the display using the interactive interface. You may
want to use this if you have a specific order of items
in your mind, and do not want to display a tree in the
middle (or simply you don't have one). The file format
is simple: each line should have an item name, and
there should be no header.
ADDITIONAL STUFF:
Parameters to provide additional layers, views, or layer data.
-V ADDITIONAL_VIEW, --additional-view ADDITIONAL_VIEW
A TAB-delimited file for an additional view to be used
in the interface. This file should contain all split
names, and values for each of them in all samples.
Each column in this file must correspond to a sample
name. Content of this file will be called 'user_view',
which will be available as a new item in the 'views'
combo box in the interface
-A ADDITIONAL_LAYERS, --additional-layers ADDITIONAL_LAYERS
A TAB-delimited file for additional layers for splits.
The first column of this file must be split names, and
the remaining columns should be unique attributes. The
file does not need to contain all split names, or
values for each split in every column. Anvi'o will try
to deal with missing data nicely. Each column in this
file will be visualized as a new layer in the tree.
GENE MODE:
Gene mode related parameters.
--gene-mode Initiate the interactive interface in 'gene mode'. In
this mode, the items are genes (instead of splits of
contigs). The following views are available: detection
(the detection value of each gene in each sample). The
mean_coverage (the mean coverage of genes). The
non_outlier_mean_coverage (the mean coverage of the
non-outlier nucleotide positions of each gene in each
sample (median absolute deviation is used to remove
outliers per gene per sample)). The
non_outlier_coverage_std view (standard deviation of
the coverage of non-outlier positions of genes in
samples). You can also choose to order items and
layers according to each one of the aforementioned
views. In addition, all layer ordering that are
available in the regular mode (i.e. the full mode
where you have contigs/splits) are also available in
'gene mode', so that, for example, you can choose to
order the layers according to 'detection', and that
would be the order according to the detection values
of splits, whereas if you choose 'genes_detections'
then the order of layers would be according to the
detection values of genes. Inspection and sequence
functionality are available (through the right-click
menu), except now sequences are of the specific gene.
Inspection has now two options available: 'Inspect
Context', which brings you to the inspection page of
the split to which the gene belongs where the
inspected gene will be highlighted in yellow in the
bottom, and 'Inspect Gene', which opens the inspection
page only for the gene and 100 nts around each side of
it (the purpose of this option is to make the
inspection page load faster if you only want to look
at the nucleotide coverage of a specific gene).
NOTICE: You can't store states or collections in 'gene
mode'. However, you still can make fake selections,
and create fake bins for your viewing convenience only
(smiley). Search options are available, and you can
even search for functions if you have them in your
contigs database. ANOTHER NOTICE: loading this mode
might take a while if your bin has many genes, and
your profile database has many samples, this is
because the gene coverages stats are computed in an
ad-hoc manner when you load this mode, we know this is
not ideal and we plan to improve that (along with
other things). If you have suggestions/complaints
regarding this mode please comment on this github
issue: https://goo.gl/yHhRei. Please refer to the
online tutorial for more information.
--inseq-stats Provide if working with INSeq/Tn-Seq genomic data.
With this, all gene level coverage stats will be
calculated using INSeq/Tn-Seq statistical methods.
-b BIN_NAME, --bin-id BIN_NAME
Bin name you are interested in.
VISUALS RELATED:
Parameters that give access to various adjustements regarding the
interface.
--view NAME Start the interface with a pre-selected view. To see a
list of available views, use --show-views flag.
--title NAME Title for the interface. If you are working with a
RUNINFO dict, the title will be determined based on
information stored in that file. Regardless, you can
override that value using this parameter.
--taxonomic-level {t_domain,t_phylum,t_class,t_order,t_family,t_genus,t_species}
The taxonomic level to use whenever relevant and/or
available. The default taxonomic level is t_genus, but
if you choose something specific, anvi'o will focus on
that whenever possible.
--split-hmm-layers When declared, this flag tells the interface to split
every gene found in HMM searches that were performed
against non-singlecopy gene HMM profiles into their
own layer. Please see the documentation for details.
--hide-outlier-SNVs During profiling, anvi'o marks positions of single-
nucleotide variations (SNVs) that originate from
places in contigs where coverage values are a bit
'sketchy'. If you would like to avoid SNVs in those
positions of splits in applicable projects you can use
this flag, and the interface would hide SNVs that are
marked as 'outlier' (although it is clearly the best
to see everything, no one will judge you if you end up
using this flag) (plus, there may or may not be some
historical data on this here:
https://github.com/meren/anvio/issues/309).
--state-autoload NAME
Automatically load previous saved state and draw tree.
To see a list of available states, use --show-states
flag.
--collection-autoload NAME
Automatically load a collection and draw tree. To see
a list of available collections, use --list-
collections flag.
--export-svg FILE_PATH
The SVG output file path.
SWEET PARAMS OF CONVENIENCE:
Parameters and flags that are not quite essential (but nice to have).
--show-views When declared, the program will show a list of
available views, and exit.
--skip-check-names For debugging purposes. You should never really need
it.
-o DIR_PATH, --output-dir DIR_PATH
Directory path for output files
--dry-run Don't do anything real. Test everything, and stop
right before wherever the developer said 'well, this
is enough testing', and decided to print out results.
--show-states When declared the program will print all available
states and exit.
--list-collections Show available collections and exit.
--skip-init-functions
When declared, function calls for genes will not be
initialized (therefore will be missing from all
relevant interfaces or output files). The use of this
flag may reduce the memory fingerprint and processing
time for large datasets.
--skip-auto-ordering When declared, the attempt to include automatically
generated orders of items based on additional data is
skipped. In case those buggers cause issues with your
data, and you still want to see your stuff and deal
with the other issue maybe later.
--distance DISTANCE_METRIC
The distance metric for the hierarchical clustering.
Only relevant if you are running the interactive
interface in "collection" mode. The default is
"euclidean".
--linkage LINKAGE_METHOD
The linkage method for the hierarchical clustering.
Only relevant if you are running the interactive
interface in "collection" mode. The default is "ward".
SERVER CONFIGURATION:
For power users.
-I IP_ADDR, --ip-address IP_ADDR
IP address for the HTTP server. The default ip address
(0.0.0.0) should work just fine for most.
-P INT, --port-number INT
Port number to use for anvi'o services. If nothing is
declared, anvi'o will try to find a suitable port
number, starting from the default port number, 8080.
--browser-path PATH By default, anvi'o will use your default browser to
launch the interactive interface. If you would like to
use something else than your system default, you can
provide a full path for an alternative browser using
this parameter, and hope for the best. For instance we
are using this parameter to call Google's experimental
browser, Canary, which performs better with demanding
visualizations.
--read-only When the interactive interface is started with this
flag, all 'database write' operations will be
disabled.
--server-only The default behavior is to start the local server, and
fire up a browser that connects to the server. If you
have other plans, and want to start the server without
calling the browser, this is the flag you need.
--password-protected If this flag is set, command line tool will ask you to
enter a password and interactive interface will be
only accessible after entering same password. This
option is recommended for shared machines like
clusters or shared networks where computers are not
isolated.
--user-server-shutdown
Allow users to shutdown an anvi'server via web
interface.
> anvi-script-reformat-fasta -h
> anvi-script-reformat-fasta -h
usage: anvi-script-reformat-fasta [-h] [-l MIN_LENGTH]
[--max-percentage-gaps PERCENTAGE]
[-i TXT FILE] [-I TXT FILE] -o FASTA FILE
[--simplify-names] [--prefix PREFIX]
[-r REPORT FILE]
FASTA FILE
Reformat FASTA file (remove contigs based on length, or based on a given list
of deflines, and/or generate an output with simpler names)
positional arguments:
FASTA FILE
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-l MIN_LENGTH, --min-len MIN_LENGTH
Minimum length of contigs to keep (contigs shorter
than this value will not be included in the output
file). The default is 0, so nothing will be removed if
you do not declare a minimum size.
--max-percentage-gaps PERCENTAGE
Maximum fraction of gaps in a sequence (any sequence
with more gaps will be removed from the output FASTA
file). The default is 100.000000.
-i TXT FILE, --exclude-ids TXT FILE
IDs to remove from the FASTA file. You cannot provide
both --keep-ids and --exclude-ids.
-I TXT FILE, --keep-ids TXT FILE
If provided, all IDs not in this file will be excluded
from the reformatted FASTA file. Any additional
filters (such as --min-len) will still be applied to
the IDs in this file. You cannot provide both
--exclude-ids and --keep-ids.
-o FASTA FILE, --output-file FASTA FILE
Output file path.
--simplify-names Edit deflines to make sure they contigs have simple
names.
--prefix PREFIX Use this parameter if you would like to add a prefix
to your contig names while simplifying them. The
prefix must be a single word (you can use underscor
character, but nothing more!).
-r REPORT FILE, --report-file REPORT FILE
Report file path. When you run this program with
`--simplify-names` flag, all changes to deflines will
be reported in this file in case you need to go back
to this information later. It is not mandatory to
declare one, but it is a very good idea to have it.
> anvi-export-splits-and-coverages -h
> anvi-export-splits-and-coverages -h
usage: anvi-export-splits-and-coverages [-h] -p PROFILE_DB -c CONTIGS_DB
[-o DIR_PATH] [-O FILENAME_PREFIX]
[--splits-mode] [--report-contigs]
[--use-Q2Q3-coverages]
Export split or contig sequences and coverages across samples stored in an
anvi'o profile database. This program is especially useful if you would like
to 'bin' your splits or contigs outside of anvi'o and import the binning
results into anvi'o using `anvi-import-collection` program.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-p PROFILE_DB, --profile-db PROFILE_DB
Anvi'o profile database
-c CONTIGS_DB, --contigs-db CONTIGS_DB
Anvi'o contigs database generated by 'anvi-gen-
contigs'
-o DIR_PATH, --output-dir DIR_PATH
Directory path for output files
-O FILENAME_PREFIX, --output-file-prefix FILENAME_PREFIX
A prefix to be used while naming the output files (no
file type extensions please; just a prefix).
--splits-mode Specify this flag if you would like to output
coverages of individual 'splits', rather than their
'parent' contig coverages.
--report-contigs By default this program reports sequences and their
coverages for 'splits'. By using this flag, you can
report contig sequences and coverages instead. For
obvious reasons, you can't use this flag with
`--splits-mode` flag.
--use-Q2Q3-coverages By default this program reports the mean coverage of a
split (or contig, see --report-contigs) for each
sample. By using this flag, you can report the mean
Q2Q3 coverage by excluding 25 percent of the
nucleotide positions with the smallest coverage
values, and 25 percent of the nucleotide positions
with the largest coverage values. The hope is that
this removes 'outlier' positions resulting from non-
specific mapping, etc. that skew the mean coverage
estimate.
> anvi-import-collection -h
> anvi-import-collection -h
usage: anvi-import-collection [-h] [-c CONTIGS_DB] [-p PAN_OR_PROFILE_DB] -C
COLLECTION_NAME [--bins-info BINS_INFO]
[--contigs-mode]
TAB DELIMITED FILE
Import an external binning result into anvi'o
positional arguments:
TAB DELIMITED FILE The input file that describes bin IDs for each split
or contig.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-c CONTIGS_DB, --contigs-db CONTIGS_DB
Anvi'o contigs database generated by 'anvi-gen-
contigs'
-p PAN_OR_PROFILE_DB, --pan-or-profile-db PAN_OR_PROFILE_DB
Anvi'o pan or profile database (and even genes
database in appropriate contexts).
-C COLLECTION_NAME, --collection-name COLLECTION_NAME
Collection name.
--bins-info BINS_INFO
Additional information for bins. The file must contain
three TAB-delimited columns, where the first one must
be a unique bin name, the second should be a 'source',
and the last one should be a 7 character HTML color
code (i.e., '#424242'). Source column must contain
information about the origin of the bin. If these bins
are automatically identified by a program like
CONCOCT, this column could contain the program name
and version. The source information will be associated
with the bin in various interfaces so in a sense it is
not *that* critical what it says there, but on the
other hand it is, becuse we should also think about
people who may end up having to work with what we put
together later.
--contigs-mode Use this flag if your binning was done on contigs
instead of splits. Please refer to the documentation
for help.
実行方法
の手順に則り進める。
1、NCBI COG(Clusters of Orthologus Groups) データベースの準備。こちらは初回のみ実行する。
anvi-setup-ncbi-cogs -T 40
dockerイメージを使っている場合、一度実行してcommitする。次回以降はそれを使えば手間が減る。
2、contig.fastaの準備とデータベース作成
2、 分析対象のメタゲノムのcontigg.fastaやbinned.fastaを準備する。配列が多すぎると階層的クラスタリングの時にエラーになるので注意する。回避するには短い配列を捨てて配列数を減らす。
補足ステップ。======================================
FASTAファイルのヘッダーのdeflinesを修正(option)する。また、サイズ選択も可能。。スペースなどあるとステップ2でエラーを起こす。
anvi-script-reformat-fasta -l 5000 -o contigs.fa input_contigs.fa
contigs.faが出力される。修正されなかった場合、ヘッダーをシンプルな名前に置換する。あとで使うアラインメントのbamファイルは、修正後のfastaを使って作っていないとエラーになる。
ヘッダやファイル名で割と一般的に使われるのが"-", "<space>", "-"などだが、これらはファイル内にあってもファイル名にあってもエラーを起こす。必ず置換しておく。アンダーバー”_”にしておけばエラーは起きない。
================================================
binned.fastaからデータベースを作成する。コンティグに関連する情報(ORFの位置、各コンティグのk-mer頻度、スプリットの開始位置と終了位置、Prodigalを使った遺伝子の機能的および分類学的アノテーションなど)のデータベースとなる。
anvi-gen-contigs-database -f binned.fasta -o contigs.db -n 'An example contigs1 datbase'
複数あるなら順番に作成
anvi-gen-contigs-database -f binned2.fasta -o contigs2.db -n 'An example contigs2 datbase'
anvi-gen-contigs-database -f binned3.fasta -o contigs3.db -n 'An example contigs3 datbase'
3、コンティグデータベースを、プラットフォームに同梱されている HMM モデル(現時点では、複数のバクテリアのシングルコピー遺伝子コレクションが公開されている)からのヒットでデコレートする。できるだけ多くスレッドを当てる。dbが複数あるなら全て行う。dbを統合するまで以後も同じ。
anvi-run-hmms -c contigs.db -T 40
- -T Maximum number of threads to use for multithreading whenever possible. Very conservatively, the default is 1. It is a good idea to not exceed the number of CPUs/ cores on your system. Plus, please be careful with this option if you are running your commands on a SGE --if you are clusterizing your runs, and asking for multiple threads to use, you may deplete your resources very fast.
4、コンティグの統計を表示(コンティグスデータベースとHMMモデルが既に作成されていること)
anvi-display-contigs-stats contigs.db
http://127.0.0.1:8080にアクセスしてstatisticsを確認する。


確認し終わったら"Ctrl + C"で停止。
5、NCBI COGを使ってコンティグスデータベースの遺伝子をアノテーションするためのプログラムanvi-run-ncbi-cogsを実行する。DIAMONDが動くので、できるだけ多くスレッドを当てる。
anvi-run-ncbi-cogs -c contigs.db --num-threads 40
6、NCBI COGを使ってコンティグスデータベースの遺伝子をアノテーションするためのプログラムanvi-run-ncbi-cogsを実行する。
anvi-get-sequences-for-gene-calls -c contigs.db -o gene-calls.fa
================================================
追加ステップ - centrifugiのランとtaxonomyのインポート(参考)
各遺伝子のtaxonomyアノテーションを持っていて、それをデータベースに入れてキュレーションしたい時に実行する。kaijuやcentrifugeが使えるが、centrifugeだと以下のようにする。ステップ6のgene-calls.faを使い、各遺伝子へのtaxonomyアノテーションを行う。centrifugeはdockerイメージにも最初からインストールされている。データベースだけ用意すればよい。
# centrifugeプリビルドデータベース(初回のみ)
wget ftp://ftp.ccb.jhu.edu/pub/infphilo/centrifuge/data/p_compressed+h+v.tar.gz
tar -zxvf p_compressed+h+v.tar.gz
#p_compressed+h+v1.cf、p_compressed+h+v2.cf、p_compressed+h+v3.cfができる。ラン時は"-x p_compressed+h+v"と指定する。
#centrifugeのrun
centrifuge -f -x p_compressed+h+v gene-calls.fa -S centrifuge_hits.tsv -p 40
#=> centrifuge_report.tsvとcentrifuge_hits.tsvができる。
#anvi'oにcentrifugeの結果を取り込む。
anvi-import-taxonomy-for-genes -c contigs.db -i centrifuge_report.tsv centrifuge_hits.tsv -p centrifuge
エラーなくランできていれば、視覚化の際にtaxonomyのオプションが利用できるようになる。
================================================
7、sortしたbamファイルとbam.baiの準備。minimap2を使うなら、
#sample1
minimap2 -R "@RG\tID:X\tLB:Y\tSM:sample1\tPL:ILLUMINA" -t 40 -ax sr \
contigs.fa sample1_R1.fq.gz sample1_R2.fq.gz \
|samtools sort -@ 40 -m 2G -O BAM - > sample1.bam \
&& samtools index -@ 8 sample1.bam
#sample2
minimap2 -R "@RG\tID:X\tLB:Y\tSM:sample2\tPL:ILLUMINA" -t 40 -ax sr \
contigs.fa sample2_R1.fq.gz sample2_R2.fq.gz \
|samtools sort -@ 40 -m 2G -O BAM - > sample2.bam \
&& samtools index -@ 8 sample2.bam
#sample3
minimap2 -R "@RG\tID:X\tLB:Y\tSM:sample3\tPL:ILLUMINA" -t 40 -ax sr \
contigs.fa sample3_R1.fq.gz sample3_R2.fq.gz \
|samtools sort -@ 40 -m 2G -O BAM - > sample3.bam \
&& samtools index -@ 8 sample3.bam
8、サンプルに関する固有の情報のデータベースの作成。サンプルのbamごとに実施する。デフォルトでは 2,500-bp より長いコンティグを処理する( --min-contig-length)。
#sample1
anvi-profile -i sample1.bam -c contigs.db --output-dir PROFILES/SAMPLE1_Profile --sample-name sample1 -T 50
#sample2
anvi-profile -i sample2.bam -c contigs.db --output-dir PROFILES/SAMPLE2_Profile --sample-name sample2 -T 50
#sample3
anvi-profile -i sample3.bam -c contigs.db --output-dir PROFILES/SAMPLE3_Profile --sample-name sample3 -T 50
もし1サンプル(one bam file)しかないなら"--cluster-contigs"をつけてランする。
ステップ2ではコンティグのデータベースcontig.dbができたが、このステップではサンプルごとのデータベースであるPROFILE.dbができる。

うまくいけばHappyが出ます。
9、8の結果をマージし、クラスタリングを実行する。1サンプルのみの場合は不要。
anvi-merge \
PROFILES/SAMPLE1_Profile/PROFILE.db \
PROFILES/SAMPLE2_Profile/PROFILE.db \
PROFILES/SAMPLE3_Profile/PROFILE.db \
-o SAMPLES-MERGED -c contigs.db --enforce-hierarchical-clustering
- --skip-hierarchical-clustering If you are not planning to use the interactive interface (or if you have other means to add a tree of contigs in the database) you may skip the step where hierarchical clustering of your items are preformed based on default clustering recipes matching to your database type.
- --enforce-hierarchical-clustering If you have more than 25,000 splits in your merged profile, anvi-merge will automatically skip the hierarchical clustering of splits (by setting --skip-hierarchical-clustering flag on). This is due to the fact that computational time required for hierarchical clustering increases exponentially with the number of items being clustered. Based on our experience we decided that 25,000 splits is about the maximum we should try. However, this is not a theoretical limit, and you can overwrite this heuristic by using this flag, which would tell anvi'o to attempt to cluster splits regardless.
versioon6+以降、ビニングは別コマンド anvi-cluster-contigsになり、このマージでは実行されなくなっている。この処理で階層的クラスタリングが実行されるが、--enforce-hierarchical-clustering をつけていてもクラスタリングに失敗することがある。失敗すると視覚化できないので、短い配列を減らすなどしてやり直す。
========================================================
追加ステップ1;コンティグを独自にビニングしている場合は、その結果をコレクションとしてマージされたプロファイルデータベースにインポートできる。
anvi-import-collection binning_results.txt -p SAMPLES-MERGED/PROFILE.db -c contigs.db --source "SOURCE_NAME"
binning_results.txtはTAB区切りのテキストファイルで、どのコンティグがどのビンに属しているかという情報を含んでいる必要がある。具体的には、コンティグ名<TAB>それが属するビン名、というタブ区切りファイルを用意する(例)。
追加ステップ2;カバレッジ情報と配列構成情報のエクスポート
anvi-export-splits-and-coverages -p SAMPLES-MERGED/PROFILE.db -c contigs.db -o output
========================================================
10、視覚化と分析。
anvi-interactive -p SAMPLES-MERGED/PROFILE.db -c contigs.db --server-only -P 8080
anvi-interactive を実行すると、各ビンの様々な特性、すなわち平均カバレッジ、分散、補完性、冗長性の推定値をその場で計算し、インタラクティブなインターフェイスでサンプル全体の分布を表示する。
http://localhost:8080にアクセスして結果を確認する。
左下のDrawボタンを押すと描画される。

単離サンプルのゲノム1つだけを分析した。複数のコンティグをクラスタリングし、環状のレイヤーにカバレッジ、GCなどを表現している。中央のデンドログラムがコンティグのクラスタリング結果を表現している。1つの環状ゲノムを表現している訳ではなく、全コンティグをカバレッジでクラスタリングして環状に並べているということ (右上1/4が注釈になっていても何も問題はない)。
環状表現からlinear phylogramに変更した。

メタゲノムアセンブリ(37,297 sequecnes、total 488,010,807-bp)

10 sample表示してます。
拡大した。カバレッジに基づいてクラスタリングされていることが分かる。

中心部のデンドログラムの枝部分にマウスホバーすると、特定のクレードだけハイライト表示される。
ハイライト表示してターゲットを定め、左クリックすることで名前をアサインできる。追加される名前はBinタブで制御する。

追加した後でも、Binタブの名前を変えれば変更可能。
BinタブでNew Binをクリックして名前を追加し、

Bin1とBin2を追加した。

興味あるクラスターが見つかったら、マウスホイールで拡大して右クリックする。

表示されるメニューの中のinspect splitからコンティグの全サンプルカバレッジを確認可能。長いコンティグはすべてsplitして扱われるため、splitt_xxxという表記になっている。

緑の線はGC%。下には予測されORFがオーバーレイ表示されている。ポジションは右上から変更可能。
右クリックからsplit配列のnrやrefseqへのblastingもできる。

ステップ6でtaxonomyをインポートしていると、taxonomyのレイヤーが最外周に追加されている。

Legendタブで色を修正可能。

LayerタブでトータルリードとSNVの色を変えた。

左のメニューから、カバレッジの表示方法について選択できる(詳細)。

abundance treeにした。カバレッジabundanceに基づいてサンプルの順番(円の中心から外周のリングの順番)が並べ替えられ、右上にそのクラスタリングのデンドログラムが追加された。

15サンプル

補足
重すぎる時は画面をリロードして下さい。ただし保存されてない設定は初期化されます。
MainのShow Advanced settingsを展開すると、図のサイズなど変更できる。

DENDROGRAMのアングル(0-270度)も変えることができる。
右下のボタンから出力すると、レジェンドつきでダウンロードディレクトリに.SVGが出力される。

引用
Anvi'o: an advanced analysis and visualization platform for 'omics data
Eren AM, Esen ÖC, Quince C, Vineis JH, Morrison HG, Sogin ML, Delmont TO
PeerJ. 2015 Oct 8;3:e1319
参考
関連