2020 11/11 extractコマンド追記
2022/11/21 登録コマンド追記
代謝、薬剤耐性、病原性などの生物学的パスウェイに関与する遺伝子は、多くの場合、遺伝子クラスターとしてクラスター化されている。相同な遺伝子クラスターを特定することは、その機能や進化の研究に役立つが、既存のツールは局所的な配列データベースの検索に限られている。また、そのためには、オンラインでのゲノムデータの急速な増加に対応するために、リモートで公開データベースを検索するためのツールが必要とされている。本研究では、Pythonベースのツールであるcblasterを用いて、ローカルデータベースとリモートデータベースのコロケーション遺伝子を迅速に検出するツールを紹介する。cblasterは比較ゲノミクスツールボックスの重要なアップデートである。
遺伝子クラスターを同一性によってグループ化すると、相同タンパク質のブロックが強調され、クラスター境界の指定や、コアとなる生合成遺伝子や機能的なサブクラスターの同定が容易になる。これは、機能的および進化的関係の有用なプロキシである。例えば、著者らは最近この技術を使用して、近縁の2つの天然物、インドロトリプトリンとインドロカルバゾールの生合成遺伝子クラスターをグループ化した。
cblasterはタンパク質配列のコレクションが与えられると、リモート(NCBI BLAST API経由)またはローカル(DIAMOND経由)で配列データベースを検索する。検索結果は解析され、identity、coverage、e-valueのユーザー定義しきい値に基づいてフィルタリングされる。残りのヒットのゲノム座標は、NCBIのIdentical Protein Group (IPG)データベース(またはローカル検索の場合はローカルデータベース)から取得される。最後に、cblasterはcollocationのインスタンスをスキャンし、可視化する。
解析の手順はプレプリントの図1にまとめられています。
インストール
macOSではエラーが出た。ubuntu18でcondaでpython3.6の環境を作ってからpipで導入した(conda create -n cblaster python=3.6)。
依存
- cblaster is tested on Python 3.6, and its only external Python dependency is the requests module (used for interaction with NCBI APIs). If you want to perform local searches, you should have diamond installed and available on your system $PATH.
pip3 install cblaster
> cblaster
$ cblaster
usage: cblaster [-h] [--version] [-d] [-i INDENT]
{gui,makedb,search,gne,extract} ...
cblaster finds co-located sequence homologues.
Documentation available at https://cblaster.readthedocs.io
Type -h/--help after either subcommand for full description of available arguments.
positional arguments:
{gui,makedb,search,gne,extract}
makedb Generate JSON/diamond databases from GenBank files
search Start a local/remote cblaster search
gne Perform gene neighbourhood estimation
extract Extract hit sequences from session files
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--version show program's version number and exit
-d, --debug Print debugging information
-i INDENT, --indent INDENT
Total spaces to use as indent in JSON file (def. None)
Cameron Gilchrist, 2020
> cblaster search -h
$ cblaster search -h
usage: cblaster search [-h] [-qf QUERY_FILE | -qi QUERY_IDS [QUERY_IDS ...]]
[-o OUTPUT] [-ohh] [-ode OUTPUT_DELIMITER]
[-odc OUTPUT_DECIMALS] [-b BINARY] [-bhh]
[-bde BINARY_DELIMITER] [-bkey {len,max,sum}]
[-bat {identity,coverage,bitscore,evalue}]
[-bdc BINARY_DECIMALS] [-p [PLOT]]
[--blast_file BLAST_FILE] [--ipg_file IPG_FILE]
[-m {local,remote}] [-db DATABASE] [-jdb JSON_DB]
[-eq ENTREZ_QUERY] [--rid RID]
[-s [SESSION_FILE [SESSION_FILE ...]]]
[-rcp [RECOMPUTE]] [-hs HITLIST_SIZE] [-g GAP]
[-u UNIQUE] [-mh MIN_HITS] [-r REQUIRE [REQUIRE ...]]
[-me MAX_EVALUE] [-mi MIN_IDENTITY] [-mc MIN_COVERAGE]
Remote/local cblaster searches.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
Input:
-qf QUERY_FILE, --query_file QUERY_FILE
Path to FASTA file containing protein sequences to be
searched
-qi QUERY_IDS [QUERY_IDS ...], --query_ids QUERY_IDS [QUERY_IDS ...]
A collection of valid NCBI sequence identifiers to be
searched
Output:
-o OUTPUT, --output OUTPUT
Write results to file
-ohh, --output_hide_headers
Hide headers when printing result output.
-ode OUTPUT_DELIMITER, --output_delimiter OUTPUT_DELIMITER
Delimiter character to use when printing result
output.
-odc OUTPUT_DECIMALS, --output_decimals OUTPUT_DECIMALS
Total decimal places to use when printing score values
-b BINARY, --binary BINARY
Generate a binary table.
-bhh, --binary_hide_headers
Hide headers in the binary table.
-bde BINARY_DELIMITER, --binary_delimiter BINARY_DELIMITER
Delimiter used in binary table (def. none = human
readable).
-bkey {len,max,sum}, --binary_key {len,max,sum}
Key function used when generating binary table cell
values.
-bat {identity,coverage,bitscore,evalue}, --binary_attr {identity,coverage,bitscore,evalue}
Hit attribute used when generating binary table cell
values.
-bdc BINARY_DECIMALS, --binary_decimals BINARY_DECIMALS
Total decimal places to use when printing score values
-p [PLOT], --plot [PLOT]
Generate a cblaster plot. If this argument is
specified with no file name, the plot will be served
using Python's HTTP server. If a file name is
specified, a static HTML file will be generated at
that path.
--blast_file BLAST_FILE
Save BLAST/DIAMOND hit table to file
--ipg_file IPG_FILE Save IPG table to file
Searching:
-m {local,remote}, --mode {local,remote}
cblaster search mode
-db DATABASE, --database DATABASE
Database to be searched. This should be either a path
to a local DIAMOND database (if 'local' is passed to
--mode) or a valid NCBI database name (def. nr)
-jdb JSON_DB, --json_db JSON_DB
Path to local JSON database created using cblaster
makedb. If this argument is provided, genomic context
will be fetched from this database instead of through
NCBI IPG.
-eq ENTREZ_QUERY, --entrez_query ENTREZ_QUERY
An NCBI Entrez search term for pre-search filtering of
an NCBI database when using command line BLASTp (i.e.
only used if 'remote' is passed to --mode); e.g.
"Aspergillus"[organism]
--rid RID Request Identifier (RID) for a web BLAST search. This
is only used if 'remote' is passed to --mode. Useful
if you have previously run a web BLAST search and want
to directly retrieve those results instead of running
a new search.
-s [SESSION_FILE [SESSION_FILE ...]], --session_file [SESSION_FILE [SESSION_FILE ...]]
Load session from JSON. If the specified file does not
exist, the results of the new search will be saved to
this file.
-rcp [RECOMPUTE], --recompute [RECOMPUTE]
Recompute previous search session using new
thresholds. The filtered session will be written to
the file specified by this argument. If this argument
is specified with no value, the session will be
filtered but not saved (e.g. for plotting purposes).
-hs HITLIST_SIZE, --hitlist_size HITLIST_SIZE
Maximum total hits to save in a BLAST search (def.
5000). Setting this value too low may result in missed
hits/clusters.
Clustering:
-g GAP, --gap GAP Maximum allowed intergenic distance (bp) between
conserved hits to be considered in the same block
(def. 20000)
-u UNIQUE, --unique UNIQUE
Minimum number of unique query sequences that must be
conserved in a hit cluster (def. 3)
-mh MIN_HITS, --min_hits MIN_HITS
Minimum number of hits in a cluster (def. 3)
-r REQUIRE [REQUIRE ...], --require REQUIRE [REQUIRE ...]
Names of query sequences that must be represented in a
hit cluster
Filtering:
-me MAX_EVALUE, --max_evalue MAX_EVALUE
Maximum e-value for a BLAST hit to be saved (def.
0.01)
-mi MIN_IDENTITY, --min_identity MIN_IDENTITY
Minimum percent identity for a BLAST hit to be saved
(def. 30)
-mc MIN_COVERAGE, --min_coverage MIN_COVERAGE
Minimum percent query coverage for a BLAST hit to be
saved (def. 50)
Example usage
-------------
Run a remote cblaster search, save the session and generate a plot:
$ cblaster search -qf query.fa -s session.json -p
Recompute a search session with new parameters:
$ cblaster search -s session.json -rcp new.json -u 4 -g 40000
Merge multiple search sessions:
$ cblaster search -s one.json two.json three.json -rcp merged.json
Perform a local search:
$ cblaster makedb $(ls folder/*.gbk) mydb
$ cblaster search -qf query.fa -db mydb.dmnd -jdb mydb.json
Save plot as a static HTML file:
$ cblaster search -s session.json -p gne.html
Kitchen sink example:
$ cblaster search --query_file query.fa \
--session_file session.json \
--plot my_plot.html \
--output summary.csv --output_decimals 2 \
--binary abspres.csv --binary_delimiter "," \
--entrez_query "Aspergillus"[orgn] \
--max_evalue 0.05 --min_identity 50 --min_coverage 70 \
--gap 50000 --unique 2 --min_hits 3 --require Gene1 Gene2
Cameron Gilchrist, 2020
> cblaster makedb -h
$ cblaster makedb -h
usage: cblaster makedb [-h] genbanks [genbanks ...] filename
positional arguments:
genbanks Path/s to GenBank files to use when building JSON/diamond
databases
filename Name to use when building JSON/diamond databases (with
extensions .json and .dmnd, respectively)
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
> cblaster gne -h
$ cblaster gne -h
usage: cblaster gne [-h] [--max_gap MAX_GAP] [--samples SAMPLES]
[--scale {linear,log}] [-o OUTPUT] [-hh] [-d DELIMITER]
[-e DECIMALS] [-p PLOT]
session
Gene neighbourhood estimation.
Repeatedly recomputes homologue clusters with different --gap values.
positional arguments:
session cblaster session file
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
Parameters:
--max_gap MAX_GAP Maximum intergenic distance (def. 100000)
--samples SAMPLES Total samples taken from max_gap (def. 100)
--scale {linear,log} Draw sampling values from a linear or log scale (def.
linear)
Output:
-o OUTPUT, --output OUTPUT
Write results to file
-hh, --hide_headers Hide headers when printing result output.
-d DELIMITER, --delimiter DELIMITER
Delimiter character to use when printing result
output.
-e DECIMALS, --decimals DECIMALS
Total decimal places to use when printing score values
-p PLOT, --plot PLOT GNE plot HTML file. The plot is generated by default;
this option will just save a static version of it.
Example usage
-------------
Maximum gap value 200Kbp, with 200 evenly distributed gap values:
$ cblaster gne session.json --max_gap 200000 --samples 200 --scale linear
Draw gap values from a log scale (gaps increase as values increase):
$ cblaster gne session.json --scale log
Save delimited tabular output:
$ cblaster gne session.json --output gne.csv --delimiter ","
Save plot as a static HTML file:
$ cblaster gne session.json -p gne.html
Cameron Gilchrist, 2020
> cblaster extract -h
$ cblaster extract -h
usage: cblaster extract [-h] [-q QUERIES [QUERIES ...]]
[-or ORGANISMS [ORGANISMS ...]]
[-sc SCAFFOLDS [SCAFFOLDS ...]] [-o OUTPUT] [-d] [-no]
[-de DELIMITER]
session
Extract information from session files
positional arguments:
session cblaster session file
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
Filters:
-q QUERIES [QUERIES ...], --queries QUERIES [QUERIES ...]
IDs of query sequences
-or ORGANISMS [ORGANISMS ...], --organisms ORGANISMS [ORGANISMS ...]
Organism names
-sc SCAFFOLDS [SCAFFOLDS ...], --scaffolds SCAFFOLDS [SCAFFOLDS ...]
Scaffold names/ranges
Output:
-o OUTPUT, --output OUTPUT
Output file name
-d, --download Fetch sequences from NCBI and write in FASTA format
-no, --name_only Do not save sequence descriptions (i.e. no genomic
coordinates)
-de DELIMITER, --delimiter DELIMITER
Sequence description delimiter
Example usage
-------------
Extract names of sequences matching a specific query:
$ cblaster extract session.json -q "Query1"
Extract, download from NCBI and write to file in FASTA format:
$ cblaster extract session.json -q "Query1" -d -o output.fasta
Extract only from specific organisms (regular expressions):
$ cblaster extract session.json -or "Aspergillus.*" "Penicillium.*"
Generate delimited table (CSV) of all hits in clusters:
$ cblaster extract session.json -de ","
Cameron Gilchrist, 2020
テストラン
ランするにはFASTA形式の配列ファイル、またはNCBIのaccession ID, GI numbersが記載されたファイルを指定する。ここではテストデータとして用意されているFASTA形式の配列ファイルを使う。
git clone https://github.com/gamcil/cblaster.git
cd /cblaster/tests
#自分のメールアドレスを登録してデータを利用する
cblaster config --email name@domain.com
cblaster search --query_file test.faa -p out.html --output summary.csv -s session.json
- -qf, --query_file Path to FASTA file containing protein sequences to be searched
- -me, --max_evalue Maximum e-value for a BLAST hit to be saved (def.
0.01) - -mi, --min_identity Minimum percent identity for a BLAST hit to be saved
(def. 30) - -mc, --min_coverage Minimum percent query coverage for a BLAST hit to be saved (def. 50)
- -u, --unique Minimum number of unique query sequences that must be conserved in a hit cluster (def. 3)
- -mh, --min_hits Minimum number of hits in a cluster (def. 3)
- -g, --gap Maximum allowed intergenic distance (bp) between conserved hits to be considered in the same block (def. 20000)
- -ode, --output_delimiter Delimiter character to use when printing result output.
- -odc, --output_decimals Total decimal places to use when printing score values
- -s, --session_file Load session from JSON. If the specified file does not exist, the results of the new search will be saved to this file.
リモートでの配列検索が実行される。
[12:26:10] INFO - Starting cblaster in remote mode
[12:26:10] INFO - Launching new search
[12:26:12] INFO - Request Identifier (RID): UPPEKFF9016
[12:26:12] INFO - Request Time Of Execution (RTOE): 27s
[12:26:39] INFO - Polling NCBI for completion status
[12:26:39] INFO - Checking search status...
[12:27:39] INFO - Checking search status...
[12:27:40] INFO - Search has completed successfully!
[12:27:40] INFO - Retrieving results for search UPPEKFF9016
[12:27:43] INFO - Parsing results...
[12:27:43] INFO - Found 6835 hits meeting score thresholds
[12:27:43] INFO - Fetching genomic context of hits
[12:28:18] WARNING - Found no hits for IPG 346263175
[12:28:18] WARNING - Found no hits for IPG 346272747
[12:28:18] WARNING - Found no hits for IPG 336900197
[12:28:18] WARNING - Found no hits for IPG 341670659
[12:28:18] WARNING - Found no hits for IPG 334707585
[12:28:18] WARNING - Found no hits for IPG 341666946
[12:28:18] WARNING - Found no hits for IPG 341669695
[12:28:18] WARNING - Found no hits for IPG 341667385
(以下省略)
出力
0%(白)から100%(青)の同一性を示すヒートマップが表示される。
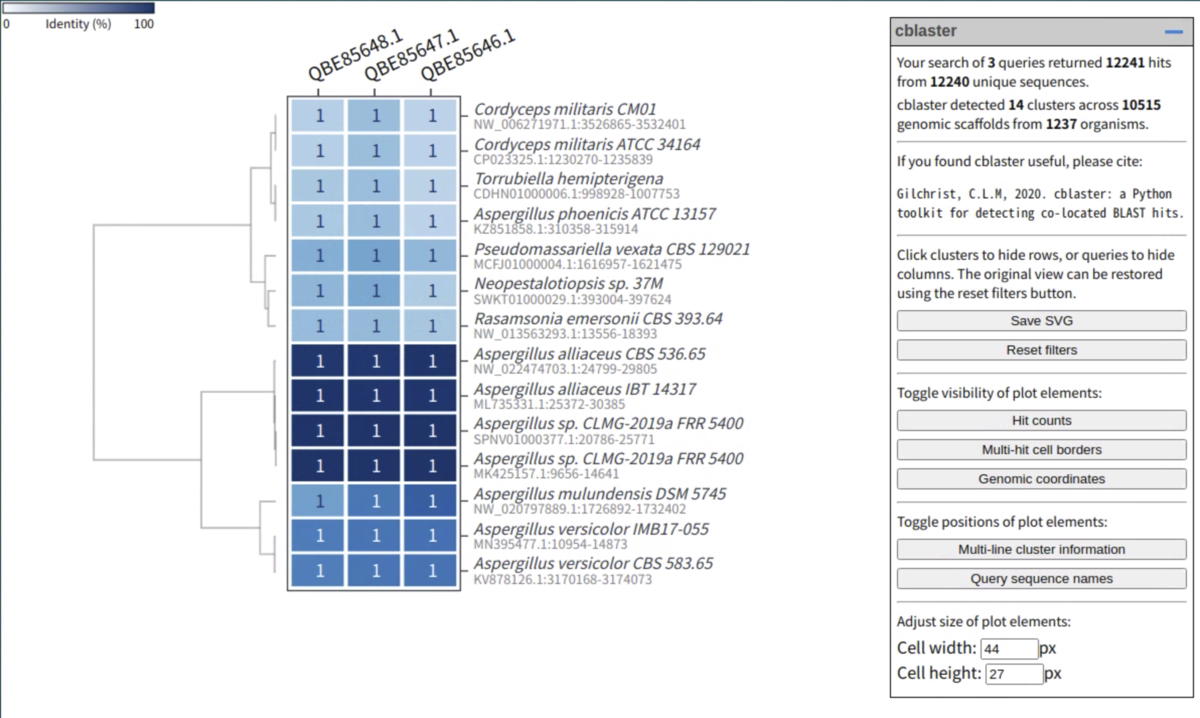
右上には
”our search of 3 queries returned 12241 hits from 12240 unique sequences.
cblaster detected 14 clusters across 10515 genomic scaffolds from 1237 organisms.”
と記載されており、14ゲノムからの遺伝子であることが分かる。
2回目以降のランならjsonファイルをロードする事で素早く視覚化できる(配列検索は終わっているので、配列検索時に使うオプションは機能しない)。
cblaster search -s session.json -p out.html
- -s, --session_file Load session from JSON. If the specified file does not exist, the results of the new search will be saved to this file.
追記
配列を取り出す。例えばクエリのQBE85647.1とマッチする配列をダウンロードする。
cblaster extract session.json -q "QBE85647.1" -d -o output.fasta
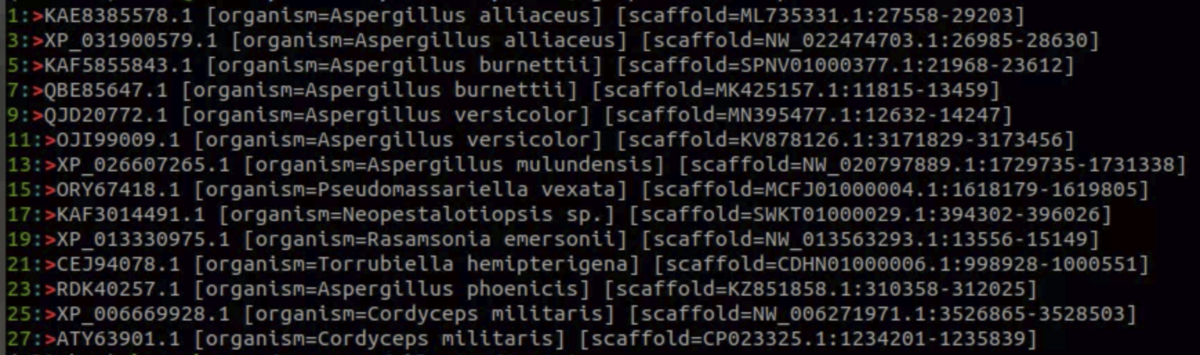
14配列ある。上手く抽出できている。
生物間でよく保存された遺伝子クラスターの配列を使うと、ヒット数が多すぎて表示が重くなる。
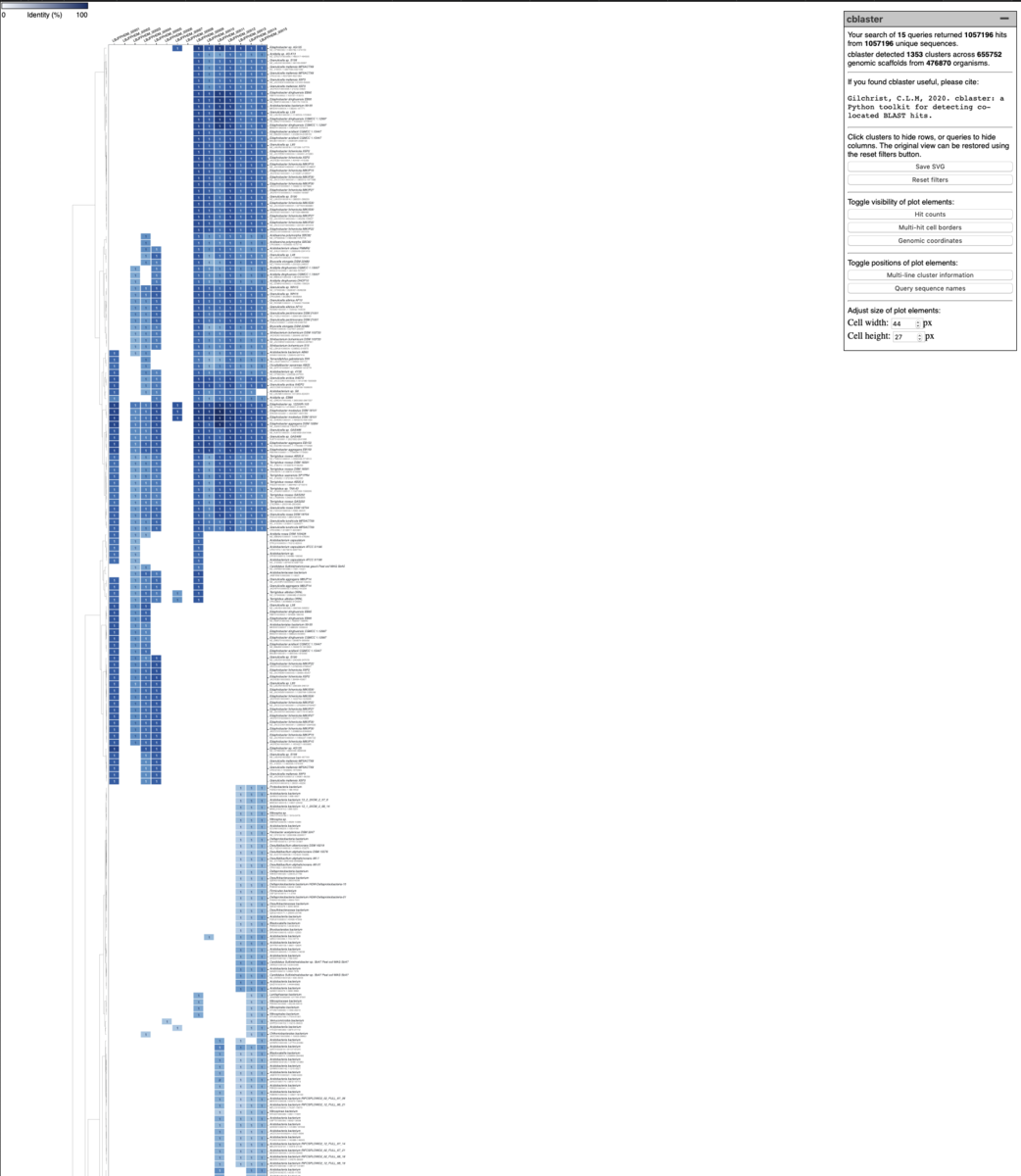
その時はBLAST検索の minimum identiyを増やしたりe-value 最大値を下げる工夫が必要と思われる。クエリの遺伝子数が多いなら"-u"や"-mh"の値を上げる事も効果的かもしれない。
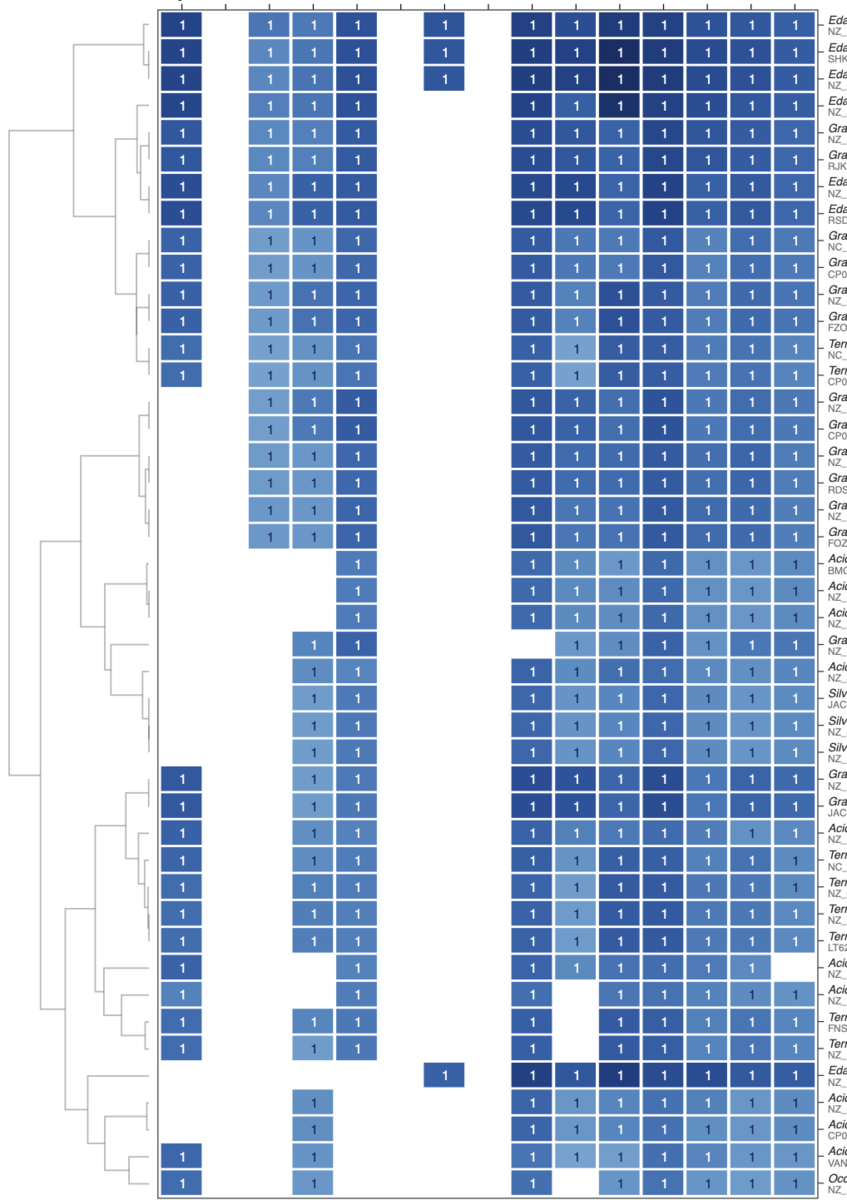
追記
少し厳しくした。
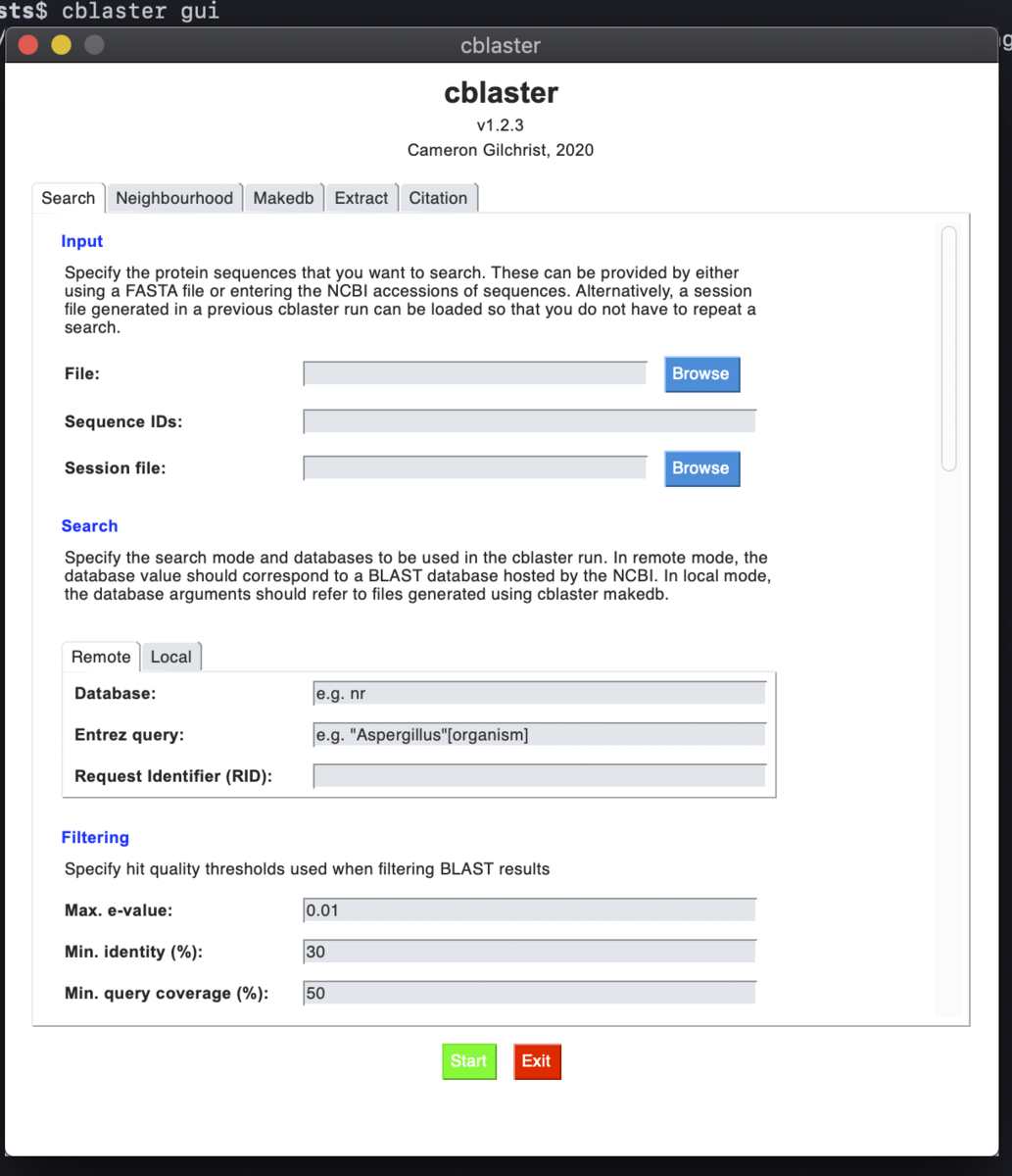
GUIバージョン
cblaster gui
引用
cblaster: a remote search tool for rapid identification and visualisation of homologous gene clusters
Cameron Laurence Mathison Gilchrist, Thomas J Booth, Yit-Heng Heng Chooi
bioRxiv, Posted November 09, 2020
追記
cblaster: a remote search tool for rapid identification and visualization of homologous gene clusters
Cameron L M Gilchrist, Thomas J Booth, Bram van Wersch, Liana van Grieken, Marnix H Medema, Yit-Heng Chooi
Bioinformatics Advances, Volume 1, Issue 1, 2021
関連